RBPMS2 Is a Myocardial-Enriched Splicing Regulator Required for Cardiac Function
- PMID: 36367103
- PMCID: PMC9770155
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321728
RBPMS2 Is a Myocardial-Enriched Splicing Regulator Required for Cardiac Function
Abstract
Background: RBPs (RNA-binding proteins) perform indispensable functions in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Numerous RBPs have been implicated in cardiac development or physiology based on gene knockout studies and the identification of pathogenic RBP gene mutations in monogenic heart disorders. The discovery and characterization of additional RBPs performing indispensable functions in the heart will advance basic and translational cardiovascular research.
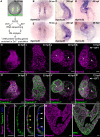
Methods: We performed a differential expression screen in zebrafish embryos to identify genes enriched in nkx2.5-positive cardiomyocytes or cardiopharyngeal progenitors compared to nkx2.5-negative cells from the same embryos. We investigated the myocardial-enriched gene RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing (variants) 2 [RBPMS2)] by generating and characterizing rbpms2 knockout zebrafish and human cardiomyocytes derived from RBPMS2-deficient induced pluripotent stem cells.
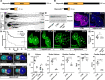
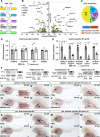
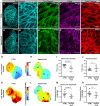
Results: We identified 1848 genes enriched in the nkx2.5-positive population. Among the most highly enriched genes, most with well-established functions in the heart, we discovered the ohnologs rbpms2a and rbpms2b, which encode an evolutionarily conserved RBP. Rbpms2 localizes selectively to cardiomyocytes during zebrafish heart development and strong cardiomyocyte expression persists into adulthood. Rbpms2-deficient embryos suffer from early cardiac dysfunction characterized by reduced ejection fraction. The functional deficit is accompanied by myofibril disarray, altered calcium handling, and differential alternative splicing events in mutant cardiomyocytes. These phenotypes are also observed in RBPMS2-deficient human cardiomyocytes, indicative of conserved molecular and cellular function. RNA-sequencing and comparative analysis of genes mis-spliced in RBPMS2-deficient zebrafish and human cardiomyocytes uncovered a conserved network of 29 ortholog pairs that require RBPMS2 for alternative splicing regulation, including RBFOX2, SLC8A1, and MYBPC3.
Conclusions: Our study identifies RBPMS2 as a conserved regulator of alternative splicing, myofibrillar organization, and calcium handling in zebrafish and human cardiomyocytes.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; alternative splicing; human induced pluripotent stem cells; myocytes, cardiac; zebrafish.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fishing Out the Role of RBPMS2 in Cardiac Splicing.Circ Res. 2022 Dec 2;131(12):1001-1003. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321922. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 36454855 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fernandez-Jimenez R, Hoit BD, Walsh RA, Fuster V, Ibanez B. Normal physiology of the cardiovascular system. In: Fuster V, editor. Hurst’s The Heart. 14th ed., McGraw Hill Education; 2017;101–124.
-
- Hajjar RJ, Ishikawa K, Thum T. Molecular and cellular biology of the heart. In: Fuster V, editor. Hurst’s The Heart. 14th ed., 2017; 125–143.
-
- Cahill TJ, Ashrafian H, Watkins H. Genetic cardiomyopathies causing heart failure. Circ Res. 2013;113:660–675. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300282 - PubMed
-
- Yotti R, Seidman CE, Seidman JG. Advances in the Genetic Basis and Pathogenesis of Sarcomere Cardiomyopathies. Annu Rev Genom Hum G. 2019;20:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-083118-015306 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

