Mst1 silencing alleviates hypertensive myocardial injury associated with the augmentation of microvascular endothelial cell autophagy
- PMID: 36367168
- PMCID: PMC9662141
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5202
Mst1 silencing alleviates hypertensive myocardial injury associated with the augmentation of microvascular endothelial cell autophagy
Abstract
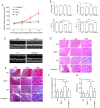
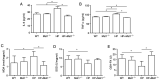
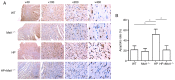
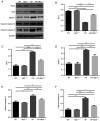
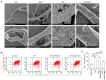
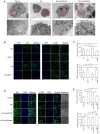
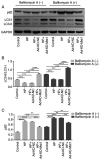
The activation of mammalian ste20‑like kinase1 (Mst1) is a crucial event in cardiac disease development. The inhibition of Mst1 has been recently suggested as a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy. However, whether silencing Mst1 also protects against hypertensive (HP) myocardial injury, or the mechanisms through which this protection is conferred are not yet fully understood. The present study aimed to explore the role of Mst1 in HP myocardial injury using in vivo and in vitro hypertension (HP) models. Angiotensin II (Ang II) was used to establish HP mouse and cardiac microvascular endothelial cell (CMEC) models. CRISPR/adenovirus vector transfection was used to silence Mst1 in these models. Using echocardiography, hematoxylin and eosin staining, Masson's trichrome staining, the enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay detection of inflammatory factors, the enzyme immunoassay detection of oxidative stress markers, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick‑end labeling staining, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, as well as immunofluorescence and western blot analysis of the autophagy markers, p62, microtubule‑associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B and Beclin‑1, it was found that Ang II induced HP myocardial injury with impaired cardiac function, increased the expression of inflammatory factors, and elevated oxidative stress in mice. In addition, it was found that Ang II reduced autophagy, enhanced apoptosis, and disrupted endothelial integrity and mitochondrial membrane potential in cultured CMECs. The silencing of Mst1 in both in vivo and in vitro HP models attenuated the HP myocardial injury. On the whole, these findings suggest that Mst1 is a key contributor to HP myocardial injury through the regulation of cardiomyocyte autophagy.
Keywords: CMEC; Mst1; autophagy; hypertension; myocardium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of melatonin on myocardial microvascular endothelial cell injury under hypertensive state by regulating Mst1.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Apr 1;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03159-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37005605 Free PMC article.
-
Mst1 knockout enhances cardiomyocyte autophagic flux to alleviate angiotensin II-induced cardiac injury independent of angiotensin II receptors.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018 Dec;125:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.028. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30193956
-
Exosomal Mst1 transfer from cardiac microvascular endothelial cells to cardiomyocytes deteriorates diabetic cardiomyopathy.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Nov;1864(11):3639-3649. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.026. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 30251683
-
Continuous Infusion of Angiotensin IV Protects against Acute Myocardial Infarction via the Inhibition of Inflammation and Autophagy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 14;2021:2860488. doi: 10.1155/2021/2860488. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34950416 Free PMC article.
-
MST1: A future novel target for cardiac diseases.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 1;239:124296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124296. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37011743 Review.
Cited by
-
GSTP1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrillation by regulating ferroptosis.Europace. 2025 May 7;27(5):euaf083. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaf083. Europace. 2025. PMID: 40186487 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA Interference Pathway: A New Target for Intervention in Different Stages of Heart Failure.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(17):1451-1463. doi: 10.2174/0115680266300535240514104107. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38798203 Review.
-
Novel Applications in Controlled Drug Delivery Systems by Integrating Osmotic Pumps and Magnetic Nanoparticles.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 31;24(21):7042. doi: 10.3390/s24217042. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39517939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Investigation of Flavonoids Targeting YBX1 Protein-Protein Interaction Network in Breast Cancer: From Computational Analysis to Experimental Validation.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 20. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01311-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39565541
-
Circular RNAs in coronary heart disease: From molecular mechanism to promising clinical application (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jan;55(1):11. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5452. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39513584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- White K, Dempsie Y, Caruso P, Wallace E, McDonald RA, Stevens H, Hatley ME, Rooij EV, Morrell NW, MacLean MR, Baker AH. Endothelial apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension is controlled by a microRNA/programmed cell death 4/caspase-3 axis. Hypertension. 2014;64:185–194. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.03037. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

