Ginsenoside Rg1 alleviates learning and memory impairments and Aβ disposition through inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome and autophagy dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice
- PMID: 36367174
- PMCID: PMC9685255
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12893
Ginsenoside Rg1 alleviates learning and memory impairments and Aβ disposition through inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome and autophagy dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice
Abstract
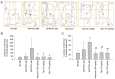
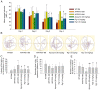
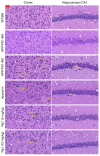
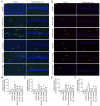
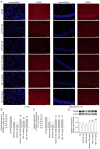
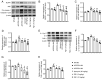
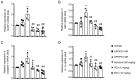
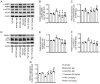
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder. Amyloid β (Aβ) deposition is considered an important pathological feature of AD. Growing evidence has linked neuroinflammation and autophagy to Aβ deposition in the progression of AD. However, there are few drug options for inhibiting neuroinflammation and autophagy to prevent AD. Ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1), a steroidal saponin extracted from ginseng, has been reported to possess multiple neuroprotective effects. The present study aimed to evaluate whether Rg1 treatment could attenuate cognitive disorders and neuronal injuries by inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome and autophagy dysfunction in an AD model of APP/PS1 mice. The results of behavioral tests indicated that Rg1 treatment for 12 weeks could significantly improve olfactory dysfunction as well as learning and memory impairments. The results of histopathological tests indicated that Rg1 treatment could reduce Aβ deposition and neuronal damages in APP/PS1‑9M mice. Additionally, the results of immunoblot, reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR or immunohistochemistry demonstrated that Rg1 treatment significantly downregulated the expression levels of inflammation‑related proteins of NLRP1, caspase1, IL‑1β and TNF‑α, as well as autophagy‑related proteins of p‑AMPK/AMPK, Beclin1 and LC3 II/LC3 I, and increased the expression levels of p‑mTOR/mTOR and P62 in APP/PS1‑9M mice. In addition, the molecular docking analysis showed that there was favorable binding result between Rg1 and NLRP1. The present study suggested that Rg1 may alleviate learning and memory impairments and Aβ disposition by inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome and improving autophagy dysfunction, suggesting that Rg1 may be a potential therapeutic agent for delaying AD.
Keywords: AMPK/mTOR; APP/PS1 mice; Alzheimer's disease; Ginsenoside Rg1; NLRP1 inflammasome; autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

