Multi-omics Investigation into the Mechanism of Action of an Anti-tubercular Fatty Acid Analogue
- PMID: 36367461
- PMCID: PMC10948109
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c08238
Multi-omics Investigation into the Mechanism of Action of an Anti-tubercular Fatty Acid Analogue
Abstract
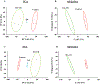
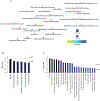
The mechanism of action (MoA) of a clickable fatty acid analogue 8-(2-cyclobuten-1-yl)octanoic acid (DA-CB) has been investigated for the first time. Proteomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics were combined with a network analysis to investigate the MoA of DA-CB against Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msm). The metabolomics results showed that DA-CB has a general MoA related to that of ethionamide (ETH), a mycolic acid inhibitor that targets enoyl-ACP reductase (InhA), but DA-CB likely inhibits a step downstream from InhA. Our combined multi-omics approach showed that DA-CB appears to disrupt the pathway leading to the biosynthesis of mycolic acids, an essential mycobacterial fatty acid for both Msm and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). DA-CB decreased keto-meromycolic acid biosynthesis. This intermediate is essential in the formation of mature mycolic acid, which is a key component of the mycobacterial cell wall in a process that is catalyzed by the essential polyketide synthase Pks13 and the associated ligase FadD32. The multi-omics analysis revealed further collateral alterations in bacterial metabolism, including the overproduction of shorter carbon chain hydroxy fatty acids and branched chain fatty acids, alterations in pyrimidine metabolism, and a predominate downregulation of proteins involved in fatty acid biosynthesis. Overall, the results with DA-CB suggest the exploration of this and related compounds as a new class of tuberculosis (TB) therapeutics. Furthermore, the clickable nature of DA-CB may be leveraged to trace the cellular fate of the modified fatty acid or any derived metabolite or biosynthetic intermediate.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
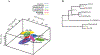
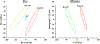



References
-
- Geneva: World Health Organization, Global tuberculosis report 2021; WHO Press, 2021
-
- Caminero JA; Matteelli A; Lange C, Treatment of TB. Eur. Respir. Monogr 2012, (58), 154–166.
-
- Chakaya J; Khan M; Ntoumi F; Aklillu E; Fatima R; Mwaba P; Kapata N; Mfinanga S; Hasnain SE; Katoto PDMC; Bulabula ANH; Sam-Agudu NA; Nachega JB; Tiberi S; McHugh TD; Abubakar I; Zumla A, Global Tuberculosis Report 2020 - Reflections on the Global TB burden, treatment and prevention efforts. Int. J. Infect. Dis 2021, 113 (Suppl._1), S7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

