Impact of COVID-19 & Response Measures on HIV-HCV Prevention Services and Social Determinants in People Who Inject Drugs in 13 Sites with Recent HIV Outbreaks in Europe, North America and Israel
- PMID: 36367613
- PMCID: PMC9651099
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-022-03851-x
Impact of COVID-19 & Response Measures on HIV-HCV Prevention Services and Social Determinants in People Who Inject Drugs in 13 Sites with Recent HIV Outbreaks in Europe, North America and Israel
Abstract
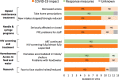
HIV/HCV prevention among people who inject drugs (PWID) is of key public health importance. We aimed to assess the impact of COVID-19 and associated response measures on HIV/HCV prevention services and socio-economic status of PWID in high-HIV-risk sites. Sites with recent (2011-2019) HIV outbreaks among PWID in Europe North America and Israel, that had been previously identified, were contacted early May 2020. Out of 17 sites invited to participate, 13 accepted. Semi-structured qualitative site reports were prepared covering data from March to May 2020, analyzed/coded and confirmed with a structured questionnaire, in which all sites explicitly responded to all 103 issues reported in the qualitative reports. Opioid maintenance treatment, needle/syringe programs and antiretroviral treatment /hepatitis C treatment continued, but with important reductions and operational changes. Increases in overdoses, widespread difficulties with food and hygiene needs, disruptions in drug supply, and increased homelessness were reported. Service programs rapidly reformed long established, and politically entrenched, restrictive service delivery policies. Future epidemic control measures should include mitigation of negative side-effects on service provision and socio-economic determinants in PWID.
La prevención del VIH/VHC entre las personas que se inyectan drogas (PWID) es de vital importancia para la salud pública. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar el impacto de COVID-19 y las medidas de respuesta asociadas en los servicios de prevención del VIH/VHC y el estado socioeconómico de las PWID en sitios de alto riesgo de VIH. Se contactó con sitios con brotes recientes (2011–2019) de VIH entre PWID en Europa, América del Norte e Israel, que habían sido previamente identificados, a principios de mayo de 2020. De los 17 sitios invitados a participar, 13 aceptaron. Se prepararon informes cualitativos semiestructurados del sitio que cubrían los datos de marzo a mayo de 2020, analizados/codificados y confirmados con un cuestionario estructurado, en el que todos los sitios respondieron explícitamente a los 103 asuntos reportados en los informes cualitativos. El tratamiento de mantenimiento con opiáceos, los programas de agujas/jeringas y el tratamiento antirretroviral/tratamiento de la hepatitis C continuaron, pero con importantes reducciones y cambios operativos. Se reportaron aumentos en las sobredosis, dificultades generalizadas con las necesidades alimentarias y de higiene, interrupciones en el suministro de medicamentos y aumento de personas sin hogar. Los programas de servicios reformaron rápidamente las políticas restrictivas de prestación de servicios, establecidas desde hace mucho tiempo y políticamente arraigadas. Las futuras medidas de control de epidemias deben incluir la mitigación de los efectos secundarios negativos en la prestación de servicios y los determinantes socioeconómicos en las PWID.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; HIV; Hepatitis C; Homelessness; Outbreaks; Overdose; People who inject drugs (PWID); Prevention; Services; Social determinants; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19 - 11 May 2022. Geneva; 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
-
- WHO. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. Geneva; 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were...
-
- United Nations. A UN framework for the immediate socio-economic response to COVID-19. April 2020. New York; 2020. Available from: https://unsdg.un.org/sites/default/files/2020-04/UN-framework-for-the-im...
-
- Degenhardt L, Peacock A, Colledge S, Leung J, Grebely J, Vickerman P, et al. Global prevalence of injecting drug use and sociodemographic characteristics and prevalence of HIV, HBV, and HCV in people who inject drugs: a multistage systematic review. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(12):e1192-e207. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30375-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical