Protein Expression of Amino Acid Transporters Is Altered in Isolated Cerebral Microvessels of 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 36367657
- PMCID: PMC9849299
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-022-03111-y
Protein Expression of Amino Acid Transporters Is Altered in Isolated Cerebral Microvessels of 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
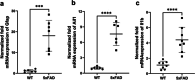
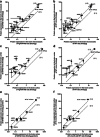
Membrane transporters such as ATP-binding cassette (ABC) and solute carrier (SLC) transporters expressed at the neurovascular unit (NVU) play an important role in drug delivery to the brain and have been demonstrated to be involved in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. However, our knowledge of quantitative changes in transporter absolute protein expression and functionality in vivo in NVU in AD patients and animal models is limited. The study aim was to investigate alterations in protein expression of ABC and SLC transporters in the isolated brain microvessels and brain prefrontal cortices of a widely used model of familial AD, 5xFAD mice (8 months old), using a sensitive liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-based quantitative targeted absolute proteomic approach. Moreover, we examined alterations in brain prefrontal cortical and plasmatic levels of transporter substrates in 5xFAD mice compared to age-matched wild-type (WT) controls. ASCT1 (encoded by Slc1a4) protein expression in the isolated brain microvessels and brain prefrontal cortices of 5xFAD mice was twice higher compared to WT controls (p = 0.01). Brain cortical levels of ASCT1 substrate, serine, were increased in 5xFAD mice compared to WT animals. LAT1 (encoded by Slc7a5) and 4F2hc (encoded by Slc3a2) protein expressions were significantly altered in the isolated brain microvessels of 5xFAD mice compared to WT controls (p = 0.008 and p = 0.05, respectively). Overall, the study provides important information, which is crucial for the optimal use of the 5xFAD mouse model in AD drug development and for investigating novel drug delivery approaches. In addition, the findings of the study shed light on the novel potential mechanisms underlying AD pathogenesis.
Keywords: 5xFAD mice; Alzheimer’s disease; Amino acids; Brain cortex; Brain microvessels; Membrane transporter.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

