Targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate cancer therapy
- PMID: 36367667
- PMCID: PMC10409967
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-022-00702-1
Targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate cancer therapy
Abstract
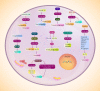
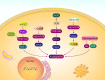
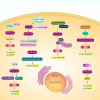
Urological cancers have obtained much attention in recent years due to their mortality and morbidity. The most common and malignant tumor of urological cancers is prostate cancer that imposes high socioeconomic costs on public life and androgen-deprivation therapy, surgery, and combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy are employed in its treatment. PI3K/Akt signaling is an oncogenic pathway responsible for migration, proliferation and drug resistance in various cancers. In the present review, the role of PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate cancer progression is highlighted. The activation of PI3K/Akt signaling occurs in prostate cancer, while PTEN as inhibitor of PI3K/Akt shows down-regulation. Stimulation of PI3K/Akt signaling promotes survival of prostate tumor cells and prevents apoptosis. The cell cycle progression and proliferation rate of prostate tumor cells increase by PI3K/Akt signaling induction. PI3K/Akt signaling stimulates EMT and enhances metastasis of prostate tumor cells. Silencing PI3K/Akt signaling impairs growth and metastasis of prostate tumor cells. Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling mediates drug resistance and reduces radio-sensitivity of prostate tumor cells. Anti-tumor compounds suppress PI3K/Akt signaling in impairing prostate tumor progression. Furthermore, upstream regulators such as miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs regulate PI3K/Akt signaling and it has clinical implications for prostate cancer patients.
Keywords: Anti-cancer agents; Cancer therapy; Chemoresistance; PI3K/Akt; Prostate cancer.
© 2022. The International CCN Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249-79. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006. PMID: 16854453
-
Progress in targeting PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis in glioblastoma therapy: Revisiting molecular interactions.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114204. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114204. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36916430 Review.
-
Biological impact and therapeutic perspective of targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: Promises and Challenges.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Jan;187:106553. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106553. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36400343 Review.
-
PI3K/Akt signaling in urological cancers: Tumorigenesis function, therapeutic potential, and therapy response regulation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 15;955:175909. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175909. Epub 2023 Jul 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37490949 Review.
-
High Efficacy of Combination Therapy Using PI3K/AKT Inhibitors with Androgen Deprivation in Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models.Eur Urol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1177-1185. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.08.053. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25220373
Cited by
-
The Potential Mechanisms of Ochratoxin A in Prostate Cancer Development: An Integrated Study Combining Network Toxicology, Machine Learning, and Molecular Docking.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Aug 4;17(8):388. doi: 10.3390/toxins17080388. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40864064 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of variant isoforms of the tyrosine kinase SYK differentially regulates cervical cancer progression through PI3K/AKT pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 23;14(1):29080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80579-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39580521 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between ferroptosis and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 21;30(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02851-6. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40685346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of CELF2 in ferroptosis: Potential targets for cancer therapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Oct;52(4):88. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5291. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37594127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Curcumin in Cancer: A Focus on the PI3K/Akt Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 18;16(8):1554. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081554. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abd Wahab NA et al (2021) Diarylpentanoid (1,5-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadiene-3-one) (MS13) Exhibits Anti-proliferative, Apoptosis Induction and Anti-migration Properties on Androgen-independent Human Prostate Cancer by Targeting Cell Cycle-Apoptosis and PI3K Signalling Pathways. Front Pharmacol 12:707335 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

