Effect of an intervention of exercise on sleep and seizure frequency in idiopathic epileptic dogs
- PMID: 36368312
- PMCID: PMC10099787
- DOI: 10.1111/jsap.13568
Effect of an intervention of exercise on sleep and seizure frequency in idiopathic epileptic dogs
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this study was to compare sleep and seizure frequency between epileptic dogs prescribed a 20% activity increase and epileptic dogs not prescribed an activity increase.
Methods: Sixty-nine dogs receiving anti-epileptic drug therapy were enrolled in a 6-month prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial with an intention-to-treat analysis. A canine activity monitoring device was used to measure activity levels and sleep scores.
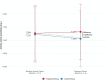
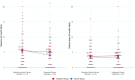
Results: Using an intention-to-treat analysis, the treatment group had an average of 0.381 more seizures per month (95% CI: 0.09 to 0.68) compared with the control group, although the difference in seizure days per month was not statistically significant. In a subgroup analysis of dogs whose activity increased by at least 10%, partial compliers had 0.719 more seizures per month (95% CI: 0.22 to 1.22) and 0.581 seizure days per month (95% CI: 0.001 to 1.16) compared with the control group. Sleep scores increased by 1.2% in the treatment compared with the control group (95% CI: 0.2 to 2.3%).
Conclusions: Seizure frequency and sleep score increased slightly, but significantly, in dogs with idiopathic epilepsy prescribed an increase in activity, compared with a control group.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Small Animal Practice published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Small Animal Veterinary Association.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors of this article has a financial or personal relationship with other people or organisations that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of the paper.
Figures


References
-
- Abadie, A. (2005) Semiparametric difference‐in‐differences estimators. Review of Economic Studies 72, 1‐19
-
- Ablah, E. , Haug, A. , Konda, K. , et al. (2009) Exercise and epilepsy: a survey of Midwest epilepsy patients. Epilepsy and Behavior 14, 162‐166 - PubMed
-
- Arida, R. M. , Cavalheiro, E. A. , Da Silva, A. C. , et al. (2008) Physical activity and epilepsy: proven and predicted benefits. Sports Medicine 38, 607‐615 - PubMed
-
- Arida, R. M. , Scorza, F. A. , Gomes da Silva, S. , et al. (2010) The potential role of physical exercise in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsy and Behavior 17, 432‐435 - PubMed

