Prevalence and factors associated with adverse drug reactions among heart failure patients hospitalized at Mbarara Regional Referral Hospital, Uganda
- PMID: 36368954
- PMCID: PMC9650824
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02937-7
Prevalence and factors associated with adverse drug reactions among heart failure patients hospitalized at Mbarara Regional Referral Hospital, Uganda
Abstract
Background: Adverse drug reaction (ADR) of medications remains an obstacle to achieving optimal disease outcomes. This study aimed to assess the prevalence and associated factors of ADR among Heart failure (HF) patients hospitalized at Mbarara Regional and Referral Hospital.
Method: A prospective observational study was conducted among hospitalized HF patients from November 2021 to January 2022. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression was employed to determine factors associated with the ADR.
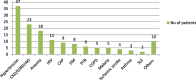
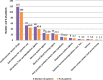
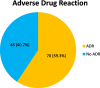
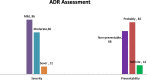
Result: Overall, 118 HF patients were included in the study with a median age of 43 years. A total of 164 ADRs were identified during the follow-up period of 1011 days. The incidence of new ADRs was 106 ADRs/1000 person-days. The prevalence of ADR was 59.3%. Of the 164 ADRs, 118(71.9%) were probable. The gastrointestinal system was the most frequently (27.5%) affected system. Over half (86, 52.4%) of the ADRs were mild and 96(58.5%) were preventable. Age group 19-59(AOR 0.15[0.03-0.35] at 95%CI, p = 0.013), herbal use (AOR 3.07[1.01-9.32] at 95%CI, p = 0.048), poly-pharmacy (AOR 8.7[2.4-15.77] at 95%CI, p < 0.001) and drug-drug interaction (AOR 6.06[2.79-12.5] at 95%CI, p = 0.004) were significantly associated with ADRs among HF patients.
Conclusion: More than half of the hospitalized HF patients experienced at least one ADR during their hospital stay. The use of herbal medicines, poly-pharmacy, and drug-drug interaction were associated with a high risk of ARDs whereas the age group 19-59 years was less likely to experience ADRs.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; Heart failure; Preventability; Severity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(4):e29–322. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:56–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

