Dominant ARF3 variants disrupt Golgi integrity and cause a neurodevelopmental disorder recapitulated in zebrafish
- PMID: 36369169
- PMCID: PMC9652361
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34354-x
Dominant ARF3 variants disrupt Golgi integrity and cause a neurodevelopmental disorder recapitulated in zebrafish
Abstract
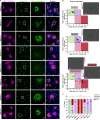
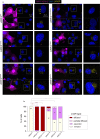
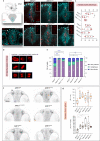
Vesicle biogenesis, trafficking and signaling via Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi network support essential developmental processes and their disruption lead to neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegeneration. We report that de novo missense variants in ARF3, encoding a small GTPase regulating Golgi dynamics, cause a developmental disease in humans impairing nervous system and skeletal formation. Microcephaly-associated ARF3 variants affect residues within the guanine nucleotide binding pocket and variably perturb protein stability and GTP/GDP binding. Functional analysis demonstrates variably disruptive consequences of ARF3 variants on Golgi morphology, vesicles assembly and trafficking. Disease modeling in zebrafish validates further the dominant behavior of the mutants and their differential impact on brain and body plan formation, recapitulating the variable disease expression. In-depth in vivo analyses traces back impaired neural precursors' proliferation and planar cell polarity-dependent cell movements as the earliest detectable effects. Our findings document a key role of ARF3 in Golgi function and demonstrate its pleiotropic impact on development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- D’Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P. ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:347–358. - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft S, et al. Phospholipase D: a downstream effector of ARF in granulocytes. Science. 1994;263:523–526. - PubMed
-
- Guo Y, Sirkis DW, Schekman R. Protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014;30:169–206. - PubMed
-
- Makhoul C, Gosavi P, Gleeson PA. The Golgi architecture and cell sensing. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018;46:1063–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

