DNA methylation predicts the outcome of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 36371196
- PMCID: PMC9652914
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03737-5
DNA methylation predicts the outcome of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 infections could be complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), increasing mortality risk. We sought to assess the methylome of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 with ARDS.
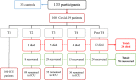
Methods: We recruited 100 COVID-19 patients with ARDS under mechanical ventilation and 33 non-COVID-19 controls between April and July 2020. COVID-19 patients were followed at four time points for 60 days. DNA methylation and immune cell populations were measured at each time point. A multivariate cox proportional risk regression analysis was conducted to identify predictive signatures according to survival.
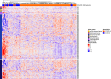
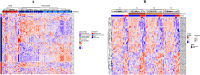
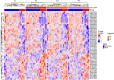
Results: The comparison of COVID-19 to controls at inclusion revealed the presence of a 14.4% difference in promoter-associated CpGs in genes that control immune-related pathways such as interferon-gamma and interferon-alpha responses. On day 60, 24% of patients died. The inter-comparison of baseline DNA methylation to the last recorded time point in both COVID-19 groups or the intra-comparison between inclusion and the end of follow-up in every group showed that most changes occurred as the disease progressed, mainly in the AIM gene, which is associated with an intensified immune response in those who recovered. The multivariate Cox proportional risk regression analysis showed that higher methylation of the "Apoptotic execution Pathway" genes (ROC1, ZNF789, and H1F0) at inclusion increases mortality risk by over twofold.
Conclusion: We observed an epigenetic signature of immune-related genes in COVID-19 patients with ARDS. Further, Hypermethylation of the apoptotic execution pathway genes predicts the outcome.
Trial registration: IMRPOVIE study, NCT04473131.
Keywords: ARDS; Biomarkers; COVID-19; DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Mortality; Survival.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C, Henry BM. Updated picture of SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations. Diagnosis (Berl) 2021;9(1):11–17. - PubMed
-
- Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429(6990):457–463. - PubMed
-
- Izquierdo AG, Carreira MC, Boughanem H, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Nicoletti CF, Oliver P, et al. Adipose tissue and blood leukocytes ACE2 DNA methylation in obesity and after weight loss. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022;52(2):e13685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

