Growth pattern in children with X-linked hypophosphatemia treated with burosumab and growth hormone
- PMID: 36371259
- PMCID: PMC9652849
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-022-02562-9
Growth pattern in children with X-linked hypophosphatemia treated with burosumab and growth hormone
Abstract
Background: X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is characterized by increased serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), hypophosphatemia and insufficient endogenous synthesis of calcitriol. Beside rickets, odonto- and osteomalacia, disproportionate short stature is seen in most affected individuals. Vitamin D analogs and phosphate supplements, i.e., conventional therapy, can improve growth especially when started early in life. Recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) therapy in XLH children with short stature has positive effects, although few reports are available. Newly available treatment (burosumab) targeting increased FGF23 signaling leads to minimal improvement of growth in XLH children. So far, we lack data on the growth of XLH children treated with concomitant rhGH and burosumab therapies.
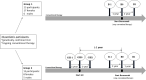
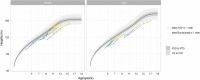
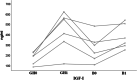
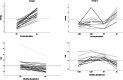
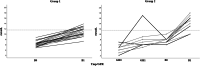
Results: Thirty-six patients received burosumab for at least 1 year after switching from conventional therapy. Of these, 23 received burosumab alone, while the others continued rhGH therapy after switching to burosumab. Children treated with burosumab alone showed a minimal change in height SDS after 1 year (mean ± SD 0.0 ± 0.3 prepubertal vs. 0.1 ± 0.3 pubertal participants). In contrast, rhGH clearly improved height during the first year of treatment before initiating burosumab (mean ± SD of height gain 1.0 ± 0.4); patients continued to gain height during the year of combined burosumab and rhGH therapies (mean ± SD height gain 0.2 ± 0.1). As expected, phosphate serum levels normalized upon burosumab therapy. No change in serum calcium levels, urinary calcium excretion, or 25-OHD levels was seen, though 1,25-(OH)2D increased dramatically under burosumab therapy.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first study on growth under concomitant rhGH and burosumab treatments. We did not observe any safety issue in this cohort of patients which is one of the largest in Europe. Our data suggest that continuing treatment with rhGH after switching from conventional therapy to burosumab, if the height prognosis is compromised, might be beneficial for the final height.
Keywords: Burosumab; Children; Growth; Recombinant human growth hormone; X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
VVZ reports speaker’s fees and travel grants from Kyowa Kirin, not related to the manuscript submitted. AL reports receiving research grant support, honoraria from Kyowa Kirin, Novo Nordisk, Sandoz, Pfizer, and Merck Serono, also not related to the manuscript submitted. The other authors have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Francis F, Hennig S, Korn B, Reinhardt R, de Jong P, Poustka A, Lehrach H, Rowe PSN, Goulding JN, Summerfield T, Mountford R, Read AP, Popowska E, Pronicka E, Davies KE, O'Riordan JLH, Econs MJ, Nesbitt T, Drezner MK, Oudet C, Pannetier S, Hanauer A, Strom TM, Meindl A, Lorenz B, Cagnoli B, Mohnike KL, Murken J, Meitinger T. A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. The HYP Consortium. Nat Genet. 1995;11:130–136. - PubMed
-
- Trombetti A, Al-Daghri N, Brandi ML, et al. Interdisciplinary management of FGF23-related phosphate wasting syndromes: a Consensus Statement on the evaluation, diagnosis and care of patients with X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022;18(6):366–384. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Tang W, Zhou J, Stubbs JR, Luo Q, Pi M, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is a counter-regulatory phosphaturic hormone for vitamin D. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN. 2006;17:1305–1315. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

