The SOD1-mediated ALS phenotype shows a decoupling between age of symptom onset and disease duration
- PMID: 36371497
- PMCID: PMC9653399
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34620-y
The SOD1-mediated ALS phenotype shows a decoupling between age of symptom onset and disease duration
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The SOD1-mediated ALS phenotype shows a decoupling between age of symptom onset and disease duration.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 2;15(1):5560. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49938-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38956107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
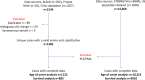
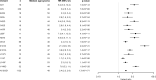
Superoxide dismutase (SOD1) gene variants may cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, some of which are associated with a distinct phenotype. Most studies assess limited variants or sample sizes. In this international, retrospective observational study, we compare phenotypic and demographic characteristics between people with SOD1-ALS and people with ALS and no recorded SOD1 variant. We investigate which variants are associated with age at symptom onset and time from onset to death or censoring using Cox proportional-hazards regression. The SOD1-ALS dataset reports age of onset for 1122 and disease duration for 883 people; the comparator population includes 10,214 and 9010 people respectively. Eight variants are associated with younger age of onset and distinct survival trajectories; a further eight associated with younger onset only and one with distinct survival only. Here we show that onset and survival are decoupled in SOD1-ALS. Future research should characterise rarer variants and molecular mechanisms causing the observed variability.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.H.V. reports to have sponsored research agreements with Biogen. P.V.D. holds a senior clinical investigatorship of FWO-Vlaanderen and is supported by the E. von Behring Chair for Neuromuscular and Neurodegenerative Disorders, the ALS Liga België and the KU Leuven funds “Een Hart voor ALS”, “Laeversfonds voor ALS Onderzoek” and the “Valéry Perrier Race against ALS Fund”. Several authors of this publication (A.C., A.L., J.W., L.B., O.H., V.S.) are members of the European Reference Network for Rare Neuromuscular Diseases (ERN-NMD). The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

