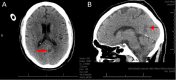
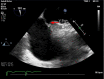
NobleStitch Patent Foramen Ovales Closure for Recurrent Strokes in a Patient with COVID-19 on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
- PMID: 36372721
- PMCID: PMC10155496
- DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2022.10.014
NobleStitch Patent Foramen Ovales Closure for Recurrent Strokes in a Patient with COVID-19 on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Keywords: COVID-19; NobleStitch; cryptogenic stroke; echocardiography; intracardiac shunt; patent foramen ovale.
Figures


References
-
- Rigatelli G, Zuin M. Managing patent foramen ovale in COVID-19 patients during and after viral infection: An unresolved matter. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2021;22:259–260. - PubMed
-
- Musuku SR, Srikanthan A, Cherukupalli D, et al. NobleStitch EL PFO closure guided by transesophageal echocardiography. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022;36:549–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

