Impact of Dolutegravir-Based Antiretroviral Therapy on Piperaquine Exposure following Dihydroartemisinin-Piperaquine Intermittent Preventive Treatment of Malaria in Pregnant Women Living with HIV
- PMID: 36374096
- PMCID: PMC9764988
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00584-22
Impact of Dolutegravir-Based Antiretroviral Therapy on Piperaquine Exposure following Dihydroartemisinin-Piperaquine Intermittent Preventive Treatment of Malaria in Pregnant Women Living with HIV
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Banda et al., "Impact of Dolutegravir-Based Antiretroviral Therapy on Piperaquine Exposure following Dihydroartemisinin-Piperaquine Intermittent Preventive Treatment of Malaria in Pregnant Women Living with HIV".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jan 24;67(1):e0156222. doi: 10.1128/aac.01562-22. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36602348 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
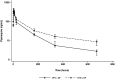
Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine, an artemisinin-based combination therapy, has been identified as a promising agent for intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy. However, in pregnant women living with HIV (PLWH), efavirenz-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) significantly reduces the plasma exposure of piperaquine. In an open-label, nonrandomized, fixed-sequence, pharmacokinetic study, we compared piperaquine plasma concentrations in 13 pregnant women during a 3-day treatment course of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine when coadministered with efavirenz-based versus dolutegravir-based ART in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. Piperaquine concentrations were measured over a 28-day period, while on efavirenz-based ART and after switching to dolutegravir-based ART. Noncompartmental analysis was performed, and geometric mean ratios (GMRs) and 90% confidence intervals (CIs) were generated to compare piperaquine pharmacokinetic parameters between these two treatment periods. Compared with efavirenz-based ART, coadministration of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and dolutegravir-based ART resulted in a 57% higher overall piperaquine exposure (area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 672 h [AUC0-672 h]) (GMR, 1.57; 90% CI, 1.28 to 1.93). Piperaquine's day 7 concentrations were also 63% higher (GMR, 1.63; 90% CI, 1.29 to 2.11), while day 28 concentrations were nearly three times higher (GMR, 2.96; 90% CI, 2.25 to 4.07). However, the maximum piperaquine concentration (Cmax) remained similar (GMR, 1.09; 90% CI, 0.79 to 1.49). Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine was well tolerated, with no medication-related serious adverse events observed in this small study. Compared with efavirenz-based ART, a known inducer of piperaquine metabolism, dolutegravir-based ART resulted in increased overall piperaquine exposure with pharmacokinetic parameter values that were similar to those published previously for pregnant and nonpregnant women. Our findings suggest that the efficacy of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine will be retained in pregnant women on dolutegravir. (The study was registered on PACTR.samrc.ac.za [PACTR201910580840196].).
Keywords: HIV; antiretroviral therapy; dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine; intermittent preventive treatment; malaria; piperaquine; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- De Beaudrap P, Turyakira E, White LJ, Nabasumba C, Tumwebaze B, Muehlenbachs A, Guérin PJ, Boum Y, McGready R, Piola P. 2013. Impact of malaria during pregnancy on pregnancy outcomes in a Ugandan prospective cohort with intensive malaria screening and prompt treatment. Malar J 12:139. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-12-139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nkhoma ET, Bowman NM, Kalilani-Phiri L, Mwapasa V, Rogerson SJ, Meshnick SR. 2012. The effect of HIV infection on the risk, frequency, and intensity of Plasmodium falciparum parasitemia in primigravid and multigravid women in Malawi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 87:1022–1027. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0392. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naniche D, Serra-Casas E, Bardaji A, Quinto L, Dobano C, Sigauque B, Cistero P, Chauhan VS, Chitnis CE, Alonso PL, Menendez C, Mayor A. 2012. Reduction of antimalarial antibodies by HIV infection is associated with increased risk of Plasmodium falciparum cord blood infection. J Infect Dis 205:568–577. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir815. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

