NAP1L5 targeting combined with MYH9 Inhibit HCC progression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 36374212
- PMCID: PMC9740361
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204377
NAP1L5 targeting combined with MYH9 Inhibit HCC progression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
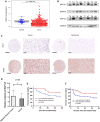
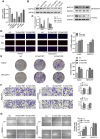
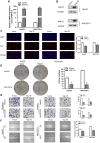
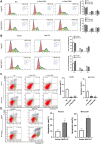
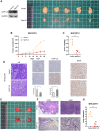
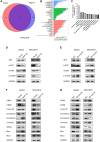
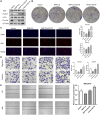
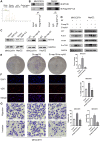
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide. Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 5 (NAP1L5) is a protein-coding gene that encodes a protein similar to nucleosome assembly protein 1 (NAP1). It is a histone chaperone that plays an important role in gene transcription in organisms. However, the role of NAP1L5 in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma remains to be elucidated. In this study, low expression of NAP1L5 was found in hepatocellular carcinoma, and the downregulation of NAP1L5 was related to shorter survival and disease-free survival. In addition, its expression is also related to the tumor size and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. The overexpression and knockdown of NAP1L5 by plasmid and siRNA showed that NAP1L5 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion and induced apoptosis of hepatoma cells. In vivo experiments confirmed that NAP1L5 can inhibit the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. In the mechanistic study, we found that NAP1L5 affects the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating MYH9 to inhibit the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. As a functional tumor suppressor, NAP1L5 is expressed at low levels in HCC. NAP1L5 inhibits the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating MYH9. It may be a new potential target for liver cancer treatment.
Keywords: MYH9; Nap1L5; hepatocellular carcinoma; invasion; migration; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha1-ACT Functions as a Tumour Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signalling Pathway via Activation of PTEN.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(6):2289-2306. doi: 10.1159/000475648. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28456796
-
[P4HA2 promotes occurrence and progression of liver cancer by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 May 20;42(5):665-672. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.05.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35673909 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Elevated PDK1 Expression Drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Promotes Radiation-Resistant and Dedifferentiated Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2020 Mar 18;9(3):746. doi: 10.3390/cells9030746. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32197467 Free PMC article.
-
[EEF1A2 inhibits the p53 function in hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/AKT/mTOR-dependent stabilization of MDM4].Pathologe. 2014 Nov;35 Suppl 2:177-84. doi: 10.1007/s00292-014-2007-y. Pathologe. 2014. PMID: 25394965 Review. German.
-
Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 May;235(5):4146-4152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29333. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31663122 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered methylation of imprinted genes in neuroblastoma: implications for prognostic refinement.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 31;22(1):808. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05634-5. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39217334 Free PMC article.
-
MALAT1-regulated gene expression profiling in lung cancer cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2023 Sep 4;23(1):818. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11347-7. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37667226 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota may affect Alzheimer's disease through synaptic function mediated by CAMs pathway: A study combining Mendelian randomization and bioinformatics.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Jan 13;9:25424823241310719. doi: 10.1177/25424823241310719. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40034528 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing ZSCAN23 promotes pancreatic cancer growth by activating Wnt signaling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2302924. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2302924. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38226836 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Muscle Myosin II A: Friend or Foe in Cancer?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9435. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179435. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akishina AA, Kuvaeva EE, Vorontsova YE, Simonova OB. NAP Family Histone Chaperones: Characterization and Role in Ontogenesis. Russ J Dev Biol. 2020; 51:343–55. 10.1134/S1062360420060028 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

