Computational perspectives on human fear and anxiety
- PMID: 36375584
- PMCID: PMC10564627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104959
Computational perspectives on human fear and anxiety
Abstract
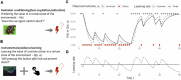
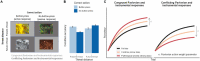
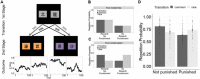
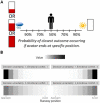
Fear and anxiety are adaptive emotions that serve important defensive functions, yet in excess, they can be debilitating and lead to poor mental health. Computational modelling of behaviour provides a mechanistic framework for understanding the cognitive and neurobiological bases of fear and anxiety, and has seen increasing interest in the field. In this brief review, we discuss recent developments in the computational modelling of human fear and anxiety. Firstly, we describe various reinforcement learning strategies that humans employ when learning to predict or avoid threat, and how these relate to symptoms of fear and anxiety. Secondly, we discuss initial efforts to explore, through a computational lens, approach-avoidance conflict paradigms that are popular in animal research to measure fear- and anxiety-relevant behaviours. Finally, we discuss negative biases in decision-making in the face of uncertainty in anxiety.
Keywords: Anxiety; Approach-avoidance conflict; Computational modelling; Decision-making; Fear; Generative models; Reinforcement learning; Uncertainty.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Approach-avoidance reinforcement learning as a translational and computational model of anxiety-related avoidance.Elife. 2023 Nov 14;12:RP87720. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87720. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37963085 Free PMC article.
-
Animal to human translational paradigms relevant for approach avoidance conflict decision making.Behav Res Ther. 2017 Sep;96:14-29. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Behav Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28495358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling Avoidance in Mood and Anxiety Disorders Using Reinforcement Learning.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Oct 1;82(7):532-539. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28343697 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking avoidance: Toward a balanced approach to avoidance in treating anxiety disorders.J Anxiety Disord. 2018 Apr;55:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Anxiety Disord. 2018. PMID: 29550689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The translational neural circuitry of anxiety.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019 Dec;90(12):1353-1360. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-321400. Epub 2019 Jun 29. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31256001 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional sophistication in human escape.iScience. 2023 Oct 18;26(11):108240. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108240. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38026199 Free PMC article.
-
Intersect between brain mechanisms of conditioned threat, active avoidance, and reward.Commun Psychol. 2025 Feb 26;3(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s44271-025-00197-7. Commun Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40011644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying aberrant approach-avoidance conflict in psychopathology: A review of computational approaches.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Apr;147:105103. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105103. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 36804398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational modeling of fear and stress responses: validation using consolidated fear and stress protocols.Front Syst Neurosci. 2024 Dec 24;18:1454336. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2024.1454336. eCollection 2024. Front Syst Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39776892 Free PMC article.
-
Cognition-enhanced geospatial decision framework integrating fuzzy FCA, surprisingly popular method, and a large language model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06508-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Vol. 5. American psychiatric association,; Washington, DC: 2013. (Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5).

