GALNT14-mediated O-glycosylation on PHB2 serine-161 enhances cell growth, migration and drug resistance by activating IGF1R cascade in hepatoma cells
- PMID: 36376274
- PMCID: PMC9663550
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05419-y
GALNT14-mediated O-glycosylation on PHB2 serine-161 enhances cell growth, migration and drug resistance by activating IGF1R cascade in hepatoma cells
Abstract
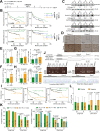
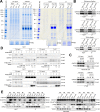
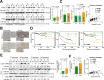
The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs9679162 located on GALNT14 gene predicts therapeutic outcomes in patients with intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the molecular mechanism remains unclear. Here, the associations between SNP genotypes, GALNT14 expression, and downstream molecular events were determined. A higher GALNT14 cancerous/noncancerous ratio was associated with the rs9679162-GG genotype, leading to an unfavorable postoperative prognosis. A novel exon-6-skipped GALNT14 mRNA variant was identified in patients carrying the rs9679162-TT genotype, which was associated with lower GALNT14 expression and favorable prognosis. Cell-based experiments showed that elevated levels of GALNT14 promoted HCC growth, migration, and resistance to anticancer drugs. Using a comparative lectin-capture glycoproteomic approach, PHB2 was identified as a substrate for GALNT14-mediated O-glycosylation. Site-directed mutagenesis experiments revealed that serine-161 (Ser161) was the O-glycosylation site. Further analysis showed that O-glycosylation of PHB2-Ser161 was required for the GALNT14-mediated growth-promoting phenotype. O-glycosylation of PHB2 was positively correlated with GALNT14 expression in HCC, resulting in increased interaction between PHB2 and IGFBP6, which in turn led to the activation of IGF1R-mediated signaling. In conclusion, the GALNT14-rs9679162 genotype was associated with differential expression levels of GALNT14 and the generation of a novel exon-6-skipped GALNT14 mRNA variant, which was associated with a favorable prognosis in HCC. The GALNT14/PHB2/IGF1R cascade modulated the growth, migration, and anticancer drug resistance of HCC cells, thereby opening the possibility of identifying new therapeutic targets against HCC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Combinations of single nucleotide polymorphisms WWOX-rs13338697, GALNT14-rs9679162 and rs6025211 effectively stratify outcomes of chemotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018 Apr;14(2):e54-e63. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12745. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28695683
-
Rs9679162 genotype predicts prognosis of real-world advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by sorafenib.Cancer Biomark. 2023;36(3):251-266. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220042. Cancer Biomark. 2023. PMID: 36938726
-
A single nucleotide polymorphism on the GALNT14 gene as an effective predictor of response to chemotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 1;134(5):1214-24. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28439. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23959947
-
GALNT14: An Emerging Marker Capable of Predicting Therapeutic Outcomes in Multiple Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 21;21(4):1491. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041491. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation-related Diagnostic and Therapeutic Drug Target Markers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2015 Sep;24(3):349-57. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.243.mew. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 26405707 Review.
Cited by
-
Aldolase B-driven lactagenesis and CEACAM6 activation promote cell renewal and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through the Warburg effect.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 10;14(10):660. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06187-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37816733 Free PMC article.
-
Proximity Labeling-Based Identification of MGAT3 Substrates and Revelation of the Tumor-Suppressive Role of Bisecting GlcNAc in Breast Cancer via GLA Degradation.Cells. 2025 Jan 12;14(2):103. doi: 10.3390/cells14020103. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851531 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting CMTM4 reverses the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and augments immunotherapy response in cervical cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jun 13;13(6):e011776. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011776. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40514067 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially functional genetic variants in ferroptosis-related CREB3 and GALNT14 genes predict survival of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2024 Jan;13(1):e6848. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6848. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38151984 Free PMC article.
-
Lactylation-Related Gene Signature Effectively Predicts Prognosis and Treatment Responsiveness in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 25;16(5):644. doi: 10.3390/ph16050644. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242427 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

