Effectiveness, Safety, and Appropriateness in the Use of the Fixed-Ratio Combination of Insulin Glargine and Lixisenatide in Type 2 Diabetes: The ENSURE Retrospective Real-World Study
- PMID: 36376644
- PMCID: PMC9663199
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-022-01328-7
Effectiveness, Safety, and Appropriateness in the Use of the Fixed-Ratio Combination of Insulin Glargine and Lixisenatide in Type 2 Diabetes: The ENSURE Retrospective Real-World Study
Abstract
Introduction: Pivotal trials documented glycemic benefits of fixed-ratio combination of insulin glargine 100 U/mL and lixisenatide (iGlarLixi), with no weight gain and low hypoglycemia risk in type 2 diabetes (T2D). This study aimed at assessing effectiveness and patterns of use of iGlarLixi in a real-world setting.
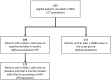
Methods: This was a retrospective, multicenter, study, based on electronic medical records. All patients initiating iGlarLixi from May 2018 to July 2020 were considered.
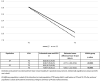
Results: Overall, 25 centers provided data on 675 patients initiating iGlarLixi with the following characteristics: age 66.4 ± 10.1 years, 54.2% men, T2D duration 15.5 ± 11.5 years, HbA1c 8.6 ± 1.4%, body mass index (BMI) 30.8 ± 5.3 kg/m2, 45.1% already treated with basal insulin, and 21.9% with basal bolus (± oral hypoglycemic agents). Metformin and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were used in 76.0% and 0.9% of patients, respectively. Combinations of iGlarLixi with other glucose-lowering drugs such as sulfonylureas or short-acting insulin were found in 32.4% of patients. Effectiveness of iGlarLixi (N = 184) showed that HbA1c declined by 0.77% [95% confidence interval (CI) -1.00, -0.54] after 6 months. In combination with metformin and/or SGLT-2i (N = 117), HbA1c declined by -0.92% (95% CI -1.22, -0.62) and weight significantly decreased by 1.21 kg. iGlarLixi dose was suboptimally titrated. Safety data (N = 171) showed incidence rates of blood glucose ≤ 70 and < 54 mg/mL of 0.26 and 0.05 events per person-month during 6 months, respectively, with a risk reduction of about 75% with respect the 6 months before iGlarLixi initiation. No severe hypoglycemia was reported.
Conclusion: In adults with T2D, effectiveness and safety of iGlarLixi were documented in a real-world setting; appropriateness of use and adequate titration should be urgently improved so that clinical practice outcomes become more comparable to clinical trials results. Further real-world studies on the effect of iGlarLixi therapy are warranted.
Keywords: Effectiveness; Fixed-ratio combination; Insulin glargine 100 U/mL; Lixisenatide; Real-world data; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources