Human Dectin-1 deficiency impairs macrophage-mediated defense against phaeohyphomycosis
- PMID: 36377664
- PMCID: PMC9663159
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI159348
Human Dectin-1 deficiency impairs macrophage-mediated defense against phaeohyphomycosis
Abstract
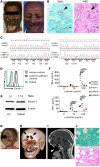
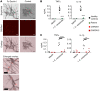
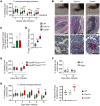
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis typically affects immunocompetent individuals following traumatic inoculation. Severe or disseminated infection can occur in CARD9 deficiency or after transplantation, but the mechanisms protecting against phaeohyphomycosis remain unclear. We evaluated a patient with progressive, refractory Corynespora cassiicola phaeohyphomycosis and found that he carried biallelic deleterious mutations in CLEC7A encoding the CARD9-coupled, β-glucan-binding receptor, Dectin-1. The patient's PBMCs failed to produce TNF-α and IL-1β in response to β-glucan and/or C. cassiicola. To confirm the cellular and molecular requirements for immunity against C. cassiicola, we developed a mouse model of this infection. Mouse macrophages required Dectin-1 and CARD9 for IL-1β and TNF-α production, which enhanced fungal killing in an interdependent manner. Deficiency of either Dectin-1 or CARD9 was associated with more severe fungal disease, recapitulating the human observation. Because these data implicated impaired Dectin-1 responses in susceptibility to phaeohyphomycosis, we evaluated 17 additional unrelated patients with severe forms of the infection. We found that 12 out of 17 carried deleterious CLEC7A mutations associated with an altered Dectin-1 extracellular C-terminal domain and impaired Dectin-1-dependent cytokine production. Thus, we show that Dectin-1 and CARD9 promote protective TNF-α- and IL-1β-mediated macrophage defense against C. cassiicola. More broadly, we demonstrate that human Dectin-1 deficiency may contribute to susceptibility to severe phaeohyphomycosis by certain dematiaceous fungi.
Keywords: Fungal infections; Genetic variation; Immunology; Infectious disease; Innate immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Yan XX, et al. CARD9 mutation linked to Corynespora cassiicola infection in a Chinese patient. Brit J Dermatol. 2015;174(1):176–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI152999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AI001175/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI143229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI134637/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N006364/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 AI121296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- 102705/Z/13/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R00 AI141622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N006364/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI148342/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/V033417/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom

