Pharmacodynamics and Bactericidal Activity of Combination Regimens in Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Application to Bedaquiline-Pretomanid-Pyrazinamide
- PMID: 36377952
- PMCID: PMC9765268
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00898-22
Pharmacodynamics and Bactericidal Activity of Combination Regimens in Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Application to Bedaquiline-Pretomanid-Pyrazinamide
Abstract
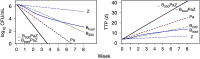
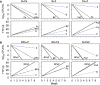
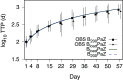
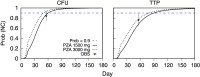
A critical barrier to codevelopment of tuberculosis (TB) regimens is a limited ability to identify optimal drug and dose combinations in early-phase clinical testing. While pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) target attainment is the primary tool for exposure-response optimization of TB drugs, the PD target is a static index that does not distinguish individual drug contributions to the efficacy of a multidrug combination. A PKPD model of bedaquiline-pretomanid-pyrazinamide (BPaZ) for the treatment of pulmonary TB was developed as part of a dynamic exposure-response approach to regimen development. The model describes a time course relationship between the drug concentrations in plasma and their individual as well as their combined effect on sputum bacillary load assessed by solid culture CFU counts and liquid culture time to positivity (TTP). The model parameters were estimated using data from the phase 2A studies NC-001-(J-M-Pa-Z) and NC-003-(C-J-Pa-Z). The results included a characterization of BPaZ activity as the most and least sensitive to changes in pyrazinamide and bedaquiline exposures, respectively, with antagonistic activity of BPa compensated by synergistic activity of BZ and PaZ. Simulations of the NC-003 study population with once-daily bedaquiline at 200 mg, pretomanid at 200 mg, and pyrazinamide at 1,500 mg showed BPaZ would require 3 months to attain liquid culture negativity in 90% of participants. These results for BPaZ were intended to be an example application with the general approach aimed at entirely novel drug combinations from a growing pipeline of new and repurposed TB drugs.
Keywords: clinical trial; combination chemotherapy; dose selection; killing kinetics; pharmacometrics; tuberculosis regimen.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
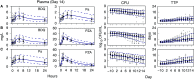
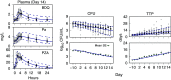
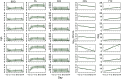
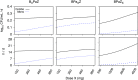
Similar articles
-
Bedaquiline-pretomanid-moxifloxacin-pyrazinamide for drug-sensitive and drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis treatment: a phase 2c, open-label, multicentre, partially randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Sep;24(9):1003-1014. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00223-8. Epub 2024 May 17. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38768617 Clinical Trial.
-
Bactericidal activity of pyrazinamide and clofazimine alone and in combinations with pretomanid and bedaquiline.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Apr 15;191(8):943-53. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1801OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 25622149 Clinical Trial.
-
Bedaquiline, moxifloxacin, pretomanid, and pyrazinamide during the first 8 weeks of treatment of patients with drug-susceptible or drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis: a multicentre, open-label, partially randomised, phase 2b trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2019 Dec;7(12):1048-1058. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30366-2. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Lancet Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 31732485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bedaquiline and delamanid in tuberculosis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(15):2319-30. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2015.1080240. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26293803 Review.
-
New Drugs for the Treatment of Tuberculosis.Clin Chest Med. 2019 Dec;40(4):811-827. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.08.001. Clin Chest Med. 2019. PMID: 31731986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A modified BPaL regimen for tuberculosis treatment replaces linezolid with inhaled spectinamides.Elife. 2024 Oct 8;13:RP96190. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96190. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39378165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dorman SE, Nahid P, Kurbatova EV, Phillips PPJ, Bryant K, Dooley KE, Engle M, Goldberg SV, Phan HTT, Hakim J, Johnson JL, Lourens M, Martinson NA, Muzanyi G, Narunsky K, Nerette S, Nguyen NV, Pham TH, Pierre S, Purfield AE, Samaneka W, Savic RM, Sanne I, Scott NA, Shenje J, Sizemore E, Vernon A, Waja Z, Weiner M, Swindells S, Chaisson RE, Tuberculosis Trials Consortium . 2021. Four-month rifapentine regimens with or without moxifloxacin for tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 384:1705–1718. 10.1056/NEJMoa2033400. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conradie F, Diacon AH, Ngubane N, Howell P, Everitt D, Crook AM, Mendel CM, Egizi E, Moreira J, Timm J, McHugh TD, Wills GH, Bateson A, Hunt R, Van Niekerk C, Li M, Olugbosi M, Spigelman M, Mvuna N, Upton C, Vanker N, Greyling L, Eriksson M, Fabiane SM, Canseco JO, Solanki P, Nix-TB Trial Team . 2020. Treatment of highly drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 382:893–902. 10.1056/NEJMoa1901814. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

