Construction and validation of a personalized nomogram of ultrasound for pretreatment prediction of breast cancer patients sensitive to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- PMID: 36378247
- PMCID: PMC9733610
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20220626
Construction and validation of a personalized nomogram of ultrasound for pretreatment prediction of breast cancer patients sensitive to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Abstract
Objective: To construct a combined radiomics model based on pre-treatment ultrasound for predicting of advanced breast cancers sensitive to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
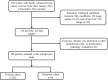
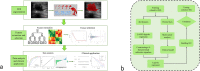
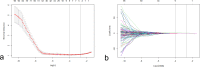
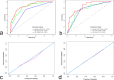
Methods: A total of 288 eligible breast cancer patients who underwent NAC before surgery were enrolled in the retrospective study cohort. Radiomics features reflecting the phenotype of the pre-NAC tumors were extracted. With features selected using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, radiomics signature (Rad-score) was established based on the pre-NAC ultrasound. Then, radiomics nomogram of ultrasound (RU) was established on the basis of the best radiomic signature incorporating independent clinical features. The performance of RU was evaluated in terms of calibration curve, area under the curve (AUC), and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: Nine features were selected to construct the radiomics signature in the training cohort. Combined with independent clinical characteristics, the performance of RU for identifying Grade 4-5 patients was significantly superior than the clinical model and Rad-score alone (p < 0.05, as per the Delong test), which achieved an AUC of 0.863 (95% CI, 0.814-0.963) in the training group and 0.854 (95% CI, 0.776-0.931) in the validation group. DCA showed that this model satisfactory clinical utility, suggesting its robustness as a response predictor.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that RU has a potential role in predicting drug-sensitive breast cancers.
Advances in knowledge: Aiming at early detection of Grade 4-5 breast cancer patients, the radiomics nomogram based on ultrasound has been approved as a promising indicator with high clinical utility. It is the first application of ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram to distinguish drug-sensitive breast cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of triple-negative breast cancer from fibroadenoma.Br J Radiol. 2022 May 1;95(1133):20210598. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210598. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35138938 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Response Prediction Using Ultrasound-Based Pre-, Post-Early, and Delta Radiomics in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 7;12:748008. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.748008. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35198437 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Multiparametric MRI Radiomics-Based Nomogram in Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer: A Two-Center study.Clin Breast Cancer. 2023 Aug;23(6):e331-e344. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2023.05.010. Epub 2023 May 27. Clin Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37321954
-
Ultrasound-based radiomics-clinical nomogram for noninvasive prediction of residual cancer burden grading in breast cancer.J Clin Ultrasound. 2024 Jun;52(5):566-574. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23666. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Clin Ultrasound. 2024. PMID: 38538081
-
Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics in the assessment of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Apr;147:95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.028. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33639324
Cited by
-
Gastrointestinal oncologic emergencies: a radiologists' guide.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jun 4. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-05012-9. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40464849 Review.
-
Progress in research on ultrasound radiomics for predicting the prognosis of breast cancer.Cancer Innov. 2023 Jul 11;2(4):283-289. doi: 10.1002/cai2.85. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cancer Innov. 2023. PMID: 38089749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with peritumoral breast tumor ultrasound radiomics: compare with intratumoral radiomics and clinicopathologic predictors.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jul;212(2):325-336. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07727-1. Epub 2025 May 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40377810 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting hormone receptor status in invasive breast cancer through radiomics analysis of long-axis and short-axis ultrasound planes.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):16503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67145-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080346 Free PMC article.
-
DCE-MRI radiomics of primary breast lesions combined with ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes for predicting efficacy of NAT.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 1;25(1):589. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14004-3. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40170181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Statistics JAC . Cancer statistics . Ca: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021. ; 71 : 7 – 33 . - PubMed
-
- Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M . Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CT neobc pooled analysis . Lancet 2019. ; 393 : 986 . - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

