Computer-Aided Imaging Analysis of Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy With Molecular Labeling and Gene Expression Identifies Markers of Response to Biological Therapy in IBD Patients: The Endo-Omics Study
- PMID: 36378498
- PMCID: PMC10472745
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izac233
Computer-Aided Imaging Analysis of Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy With Molecular Labeling and Gene Expression Identifies Markers of Response to Biological Therapy in IBD Patients: The Endo-Omics Study
Abstract
Background: We aimed to predict response to biologics in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) using computerized image analysis of probe confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) in vivo and assess the binding of fluorescent-labeled biologics ex vivo. Additionally, we investigated genes predictive of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) response.
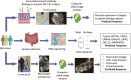
Methods: Twenty-nine patients (15 with Crohn's disease [CD], 14 with ulcerative colitis [UC]) underwent colonoscopy with pCLE before and 12 to 14 weeks after starting anti-TNF or anti-integrin α4β7 therapy. Biopsies were taken for fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled infliximab and vedolizumab staining and gene expression analysis. Computer-aided quantitative image analysis of pCLE was performed. Differentially expressed genes predictive of response were determined and validated in a public cohort.
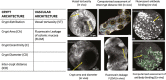
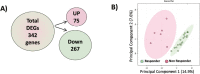
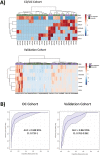
Results: In vivo, vessel tortuosity, crypt morphology, and fluorescein leakage predicted response in UC (area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve [AUROC], 0.93; accuracy 85%, positive predictive value [PPV] 89%; negative predictive value [NPV] 75%) and CD (AUROC, 0.79; accuracy 80%; PPV 75%; NPV 83%) patients. Ex vivo, increased binding of labeled biologic at baseline predicted response in UC (UC) (AUROC, 83%; accuracy 77%; PPV 89%; NPV 50%) but not in Crohn's disease (AUROC 58%). A total of 325 differentially expressed genes distinguished responders from nonresponders, 86 of which fell within the most enriched pathways. A panel including ACTN1, CXCL6, LAMA4, EMILIN1, CRIP2, CXCL13, and MAPKAPK2 showed good prediction of anti-TNF response (AUROC >0.7).
Conclusions: Higher mucosal binding of the drug target is associated with response to therapy in UC. In vivo, mucosal and microvascular changes detected by pCLE are associated with response to biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. Anti-TNF-responsive UC patients have a less inflamed and fibrotic state pretreatment. Chemotactic pathways involving CXCL6 or CXCL13 may be novel targets for therapy in nonresponders.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; RNA transcriptomics; artificial intelligence; biological agents; endoscopic molecular labeling; probe confocal laser endomicroscopy; ulcerative colitis.
© 2022 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In-Depth Assessment of Endoscopic Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated by Anti-TNF or Vedolizumab.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Feb 1;30(2):240-246. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad066. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 37042951
-
Pharmacodynamic mechanisms behind a refractory state in inflammatory bowel disease.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 17;22(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02559-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36384462 Free PMC article.
-
Low TREM1 expression in whole blood predicts anti-TNF response in inflammatory bowel disease.EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:733-742. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.027. Epub 2019 Jan 24. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30685385 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of confocal laser endomicroscopy for assessment and monitoring of therapeutic response in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Dan Med J. 2016 Nov;63(11):B5301. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27808042 Review.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Endoscopy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 31;13(15):2547. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152547. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Coloproctology: A Review of Emerging Technologies and Clinical Applications.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 30;13(19):5842. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195842. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision medicine and drug optimization in adult inflammatory bowel disease patients.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 May 10;16:17562848231173331. doi: 10.1177/17562848231173331. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37197397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Kono-S anastomosis on reducing postoperative recurrence rates in Crohn's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Tech Coloproctol. 2024 Sep 18;28(1):127. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-02991-7. Tech Coloproctol. 2024. PMID: 39289220
-
Rediscovering histology - the application of artificial intelligence in inflammatory bowel disease histologic assessment.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 17;18:17562848251325525. doi: 10.1177/17562848251325525. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40098604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ben-Horin S, Kopylov U, Chowers Y.. Optimizing anti-TNF treatments in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(1):24-30. - PubMed
-
- Amiot A, Grimaud J-C, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. ; Observatory on Efficacy and of Vedolizumab in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Study Group. Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(11):1593-1601.e2. - PubMed
-
- Wils P, Bouhnik Y, Michetti P, et al. ; Groupe d'Etude Thérapeutique des Affections Inflammatoires du Tube Digestif. Subcutaneous ustekinumab provides clinical benefit for two-thirds of patients with crohn’s disease refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):242-50.e1-2. - PubMed
-
- Stevens TW, Matheeuwsen M, Lönnkvist MH, et al. . Systematic review: predictive biomarkers of therapeutic response in inflammatory bowel disease-personalised medicine in its infancy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48(11-12):1213-1231. - PubMed
-
- Boyapati RK, Kalla R, Satsangi J, Ho G-T.. Biomarkers in search of precision medicine in IBD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(12):1682-1690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

