Pancreatectomy with resection and reconstruction of the superior mesenteric artery
- PMID: 36378526
- PMCID: PMC10361681
- DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znac363
Pancreatectomy with resection and reconstruction of the superior mesenteric artery
Figures
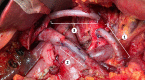
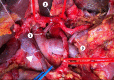
References
-
- Egawa S, Takeda K, Fukuyama S, Motoi F, Sunamura M, Matsuno S. Clinicopathological aspects of small pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2004;28:235–240 - PubMed
-
- Yoshiya S, Fukuzawa K, Inokuchi S, Kosai-Fujimoto Y, Sanefuji K, Iwaki Ket al. . Efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in distal pancreatectomy with en bloc celiac axis resection (DP-CAR) for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 2020;24:1605–1611 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

