The miR-124-AMPAR pathway connects polygenic risks with behavioral changes shared between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
- PMID: 36379214
- PMCID: PMC10183200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.031
The miR-124-AMPAR pathway connects polygenic risks with behavioral changes shared between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
Abstract
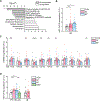
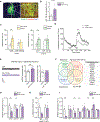
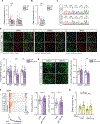
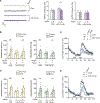
Schizophrenia (SZ) and bipolar disorder (BP) are highly heritable major psychiatric disorders that share a substantial portion of genetic risk as well as their clinical manifestations. This raises a fundamental question of whether, and how, common neurobiological pathways translate their shared polygenic risks into shared clinical manifestations. This study shows the miR-124-3p-AMPAR pathway as a key common neurobiological mediator that connects polygenic risks with behavioral changes shared between these two psychotic disorders. We discovered the upregulation of miR-124-3p in neuronal cells and the postmortem prefrontal cortex from both SZ and BP patients. Intriguingly, the upregulation is associated with the polygenic risks shared between these two disorders. Seeking mechanistic dissection, we generated a mouse model that upregulates miR-124-3p in the medial prefrontal cortex. We demonstrated that the upregulation of miR-124-3p increases GRIA2-lacking calcium-permeable AMPARs and perturbs AMPAR-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission, leading to deficits in the behavioral dimensions shared between SZ and BP.
Keywords: AMPAR; bipolar disorder; miR-124; polygenic risk; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests. R.L.H. is a member of the journal’s advisory board.
Figures

Comment in
-
A shared pathway connects schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023 Jan;24(1):2. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00662-w. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36446901 No abstract available.
-
miR-124-3p mediates polygenic risk shared between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Neuron. 2023 Jan 18;111(2):144-146. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.12.024. Neuron. 2023. PMID: 36657396
Similar articles
-
miR-124-3p mediates polygenic risk shared between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Neuron. 2023 Jan 18;111(2):144-146. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.12.024. Neuron. 2023. PMID: 36657396
-
Genetic risk for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia predicts structure and function of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021 Jul 22;46(4):E441-E450. doi: 10.1503/jpn.200165. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34291628 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex of individuals affected with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders.Schizophr Res. 2010 Dec;124(1-3):183-91. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.07.002. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Schizophr Res. 2010. PMID: 20675101 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging pattern of shared polygenic architecture of psychiatric disorders, conceptual and methodological challenges.Psychiatr Genet. 2019 Oct;29(5):152-159. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000234. Psychiatr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31464996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox dysregulation in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: insights from animal models.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Apr 20;18(12):1428-43. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4858. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22938092 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics factors in schizophrenia: future directions for etiologic and therapeutic study approaches.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 4;24(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12991-025-00557-x. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40186258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles miR- 182 - 5p Is a Potential Biomarker for Diagnosing Major Depressive Disorder.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04948-9. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40261603
-
Reversible synaptic adaptations in a subpopulation of murine hippocampal neurons following early-life seizures.J Clin Invest. 2024 Jan 16;134(5):e175167. doi: 10.1172/JCI175167. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38227384 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Olfactory neuroepithelium-derived cellular models to study neurological and psychiatric disorders.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 9;17:1203466. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1203466. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37250419 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inflammation-related pathology in the olfactory epithelium: its impact on the olfactory system in psychotic disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 May;29(5):1453-1464. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02425-8. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38321120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Consortium T.S.W.G.o.t.P.G., Ripke S, Walters JT, and O’Donovan MC (2020). Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic biology in schizophrenia. medRxiv, 2020.2009.2012.20192922. 10.1101/2020.09.12.20192922. - DOI
-
- Mullins N, Forstner AJ, O’Connell KS, Coombes B, Coleman JRI, Qiao Z, Als TD, Bigdeli TB, Børte S, Bryois J, et al. (2021). Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat Genet 53, 817–829. 10.1038/s41588-021-00857-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

