Does reverse mentoring work in the NHS: a feasibility study of clinicians in practice
- PMID: 36379653
- PMCID: PMC9668021
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-062361
Does reverse mentoring work in the NHS: a feasibility study of clinicians in practice
Abstract
Objective: To assess the risks and benefits of reverse mentoring of consultants by junior doctors.
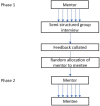
Design: A feasibility study divided into two phases: first a semistructured interview where performance of participating consultants was assessed by junior doctors and then a second phase allowing for feedback to be given on a one-to-one basis. Data collected through questionnaires with free text questions and Likert scores.
Setting: Tertiary teaching hospital in the UK.
Participants: Six junior doctors (66.6% male, age range 31-40 years) and five consultants (80% male, age range 35-65 years and consultants for 5-20 years).
Intervention: Reverse mentoring session.
Main outcome measure: The concerns and/or benefits of the process of reverse mentoring. Confidence was assessed in 7 domains: clinical practice, approach to juniors, approachability, use of technology, time management, strengths and areas for improvement using Likert scales giving a total out of 35.
Results: The most common concerns cited were overcoming the hierarchical difference and a selection bias in both mentors and mentees. However, no participant experienced this hierarchical difference through the reverse mentoring process and no relationships were negatively affected. Mentors became more confident in feeding back to seniors (23 vs 29 out of 35, p=0.04) most evident in clinical practice and areas to improve (3 vs 4 out of 5, p=0.041 and 3 vs 5 out of 5, p=0.041, respectively).
Conclusion: We present the first study of reverse mentoring in an NHS clinical setting. Initial concerns with regard to damaged relationships and hierarchical gradients were not experienced and all participants perceived that they benefited from the process. Reverse mentoring can play a role in engaging and training future leaders at junior stages and provide a means for consultants to receive valuable feedback from junior colleagues.
Keywords: education & training (see medical education & training); general medicine (see internal medicine); medical education & training; surgery.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Greengard S. Moving forward with reverse mentoring. Workforce 2002;81:15.
-
- Harvey M, Buckley MR. Assessing the “Conventional Wisdoms” of Management for the 21st Century Organization. Organ Dyn 2002;30:368–78. 10.1016/S0090-2616(02)00062-1 - DOI
-
- Marcinkus Murphy W, Murphy W. Reverse mentoring at work: fostering cross-generational learning and developing millennial leaders. Hum Resour Manage 2012;51:549–73. 10.1002/hrm.21489 - DOI
-
- Hewlett S. Let Gen Y teach you tech: Harvard business review, 2009. Available: https://hbr.org/2009/06/let-gen-y-teach-you-tech
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources