Systematic review of primary and booster COVID-19 sera neutralizing ability against SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant
- PMID: 36379935
- PMCID: PMC9665011
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-022-00565-y
Systematic review of primary and booster COVID-19 sera neutralizing ability against SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant
Abstract
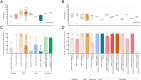
Virus neutralization data using post-vaccination sera are an important tool in informing vaccine use policy decisions, however, they often pose interpretive challenges. We systematically reviewed the pre-print and published literature for neutralization studies against Omicron using sera collected after both primary and booster vaccination. We found a high proportion of post-primary vaccination sera were not responding against Omicron but boosting increased both neutralizing activity and percent of responding sera. We recommend reporting percent of responders alongside neutralization data to portray vaccine neutralization ability more accurately.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.M.H. reports research grants from Pfizer for unrelated work; M.D.K. reports research grants from Pfizer and Merck and consultancy fees from Merck, all for unrelated work; N.B.Z. reports research grants from Merck, from Johnson & Johnson and from Serum Institute of India, all for unrelated work; and consulting fees from Merck for unrelated work. The rest of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern, https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.... (2021).
-
- ECDC. SARS-CoV-2 Variants Dashboard, https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/situation-updates/variants-dashboard (2022).
-
- CDC. COVID Data Tracker, https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions (2022).
-
- Jacobsen, H. et al. Diminished neutralization responses towards SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VoC after mRNA or vector-based COVID-19 vaccinations. Preprint at https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.21.21267898v1 (2021). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

