Thermophysical properties of the regolith on the lunar far side revealed by the in situ temperature probing of the Chang'E-4 mission
- PMID: 36381216
- PMCID: PMC9646997
- DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwac175
Thermophysical properties of the regolith on the lunar far side revealed by the in situ temperature probing of the Chang'E-4 mission
Abstract
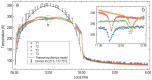
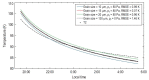
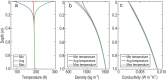
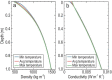
Temperature probes onboard the Chang'E-4 (CE-4) spacecraft provide the first in situ regolith temperature measurements from the far side of the Moon. We present these temperature measurements with a customized thermal model and reveal the particle size of the lunar regolith at the CE-4 landing site to be ∼15 μm on average over depth, which indicates an immature regolith below the surface. In addition, the conductive component of thermal conductivity is measured as ∼1.53 × 10-3 W m-1 K-1 on the surface and ∼8.48 × 10-3 W m-1 K-1 at a depth of 1 m. The average bulk density is ∼471 kg m-3 on the surface and ∼824 kg m-3 in the upper 30 cm of the lunar regolith. These thermophysical properties provide important additional 'ground truth' at the lunar far side, which is critical for the future analysis and interpretation of global temperature observations.
Keywords: Chang’E-4; lunar far side; regolith; temperature; thermal conductivity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Gundlach B, Blum J. A new method to determine the grain size of planetary regolith. Icarus 2013; 223: 479–92. 10.1016/j.icarus.2012.11.039 - DOI
-
- Cremers CJ, Birkebak RC. Thermal conductivity of fines from Apollo 12. In: Proceedings of the Second Lunar Science Conference. New York: Pergamon Press, 1971, 2311–15.
-
- Cremers CJ, Hsia HS. Thermal conductivity and diffusivity of Apollo 15 fines at low density. In: Proceedings of the Fourth Lunar Science Conference, New York: Pergamon Press, 1973, 2459–64.
-
- Hayne PO, Bandfield JL, Siegler MAet al. . Global regolith thermophysical properties of the moon from the Diviner lunar radiometer experiment. J Geophys Res Planets 2017; 122: 2371–400. 10.1002/2017JE005387 - DOI
-
- Yu SR, Fa WZ. Thermal conductivity of surficial lunar regolith estimated from lunar reconnaissance orbiter Diviner radiometer data. Planet Space Sci 2016; 124: 48–61. 10.1016/j.pss.2016.02.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
