Conditioned Taste Aversion to L-Amino Acid Taste Stimuli and Oral Transcriptional Changes to Type 1 Taste Receptors T1R1 and T1R3 on Chronic Exposure to L-Alanine Solution in Chickens
- PMID: 36382058
- PMCID: PMC9596290
- DOI: 10.2141/jpsa.0210128
Conditioned Taste Aversion to L-Amino Acid Taste Stimuli and Oral Transcriptional Changes to Type 1 Taste Receptors T1R1 and T1R3 on Chronic Exposure to L-Alanine Solution in Chickens
Abstract
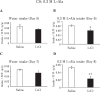
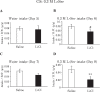
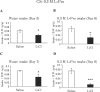
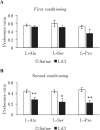
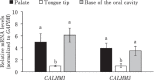
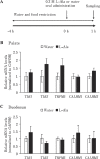
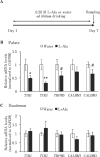
Elucidating taste sensing systems in chickens is an important step toward understanding poultry nutrition. Amino acid taste receptors, type 1 taste receptors 1 and 3 (T1R1 and T1R3, respectively), are expressed in chicken taste cells, and chicken T1R1/T1R3 is activated by L-alanine (L-Ala) and L-serine (L-Ser), but not by L-proline (L-Pro). However, it is not clear whether chickens have a gustatory perception of L-amino acids. Here, we found that chickens conditioned to avoid either L-Ala, L-Ser, or L-Pro solutions could successfully learn to avoid the corresponding L-amino acid solution in the conditioned taste aversion (CTA) test. Because CTA is a well-established learning paradigm generated specifically by pairing gustatory perception and gastrointestinal malaise, the present study suggests that chickens can sense L-amino acids by gustatory perception. In addition, we found that the expression of the T1R1 and T1R3 genes was significantly downregulated in response to chronic exposure to L-Ala solution, but not to acute oral stimulation. Taken together, the present study suggests that chickens have a gustatory perception of L-amino acids, and the expression of T1R1/T1R3 mRNAs in the oral cavity can be regulated by L-amino acid intake. Since chickens can detect L-Pro solutions, additional amino acid receptors, other than T1R1/T1R3, may be involved in L-amino acid taste detection in chickens.
Keywords: amino acid; chicken; taste; taste receptor; umami.
2022, Japan Poultry Science Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bystrova MF, Romanov RA, Rogachevskaja OA, Churbanov GD and Kolesnikov SS. Functional expression of the extracellular-Ca2+-sensing receptor in mouse taste cells. Journal of Cell Science, 123: 972-982. 2010. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhari N, Landin AM and Roper SD. A metabotropic glutamate receptor variant functions as a taste receptor. Nature Neuroscience, 3: 113-119. 2000. - PubMed
-
- Cheled-Shoval SL, Behrens M, Meyerhof MW, Niv MY and Uni Z. Perinatal administration of a bitter tastant influences gene expression in chicken palate and duodenum. Poultry Science, 62: 12512-12520. 2014. - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Yan J, Suo Y, Li J, Wang Q and Lv B. Nutritional status alters saccharin intake and sweet receptor mRNA expression in rat taste buds. Brain Research, 1325: 53-62. 2010. - PubMed

