Comprehensive characterization of elevated tau PET signal in the absence of amyloid-beta
- PMID: 36382220
- PMCID: PMC9651027
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac272
Comprehensive characterization of elevated tau PET signal in the absence of amyloid-beta
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Comprehensive characterization of elevated tau PET signal in the absence of amyloid-beta.Brain Commun. 2023 Jan 24;5(1):fcad012. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad012. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 36714325 Free PMC article.
Abstract
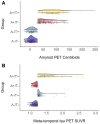
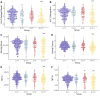
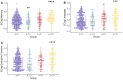
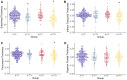
Recently proposed biomarker-only diagnostic frameworks propose that amyloid-beta is necessary for placement on the Alzheimer's disease continuum, whereas tau in the absence of amyloid-beta is considered to be a non-Alzheimer's disease pathologic change. Similarly, the pathologic designation of tau in the absence of amyloid-beta is characterized as primary age-related tauopathy and separable from Alzheimer's disease. Our study sought to identify an early-to-moderate tau stage with minimal amyloid-beta using PET imaging and characterize these individuals in terms of clinical, cognitive and biological features. Seven hundred and three participants from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative were classified into one of the four groups (A-/T-, A-/T+, A+/T- and A+/T+) based on PET positivity or negativity for cortical amyloid-beta (A-/A+) and early-to-moderate stage (i.e. meta-temporal) tau (T-/T+). These groups were then compared on demographic and clinical features, vascular risk, multi-domain neuropsychological performance, multi-domain subjective cognitive complaints, apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 carrier status and cortical thickness across Alzheimer's disease-vulnerable regions. The proportion of participants classified in each group was as follows: 47.23% A-/T-, 13.51% A-/T+, 12.23% A+/T- and 27.03% A+/T+. Results indicated that the A-/T+ and A+/T+ groups did not statistically differ on age, sex, depression levels, vascular risk and cortical thickness across temporal and parietal regions. Additionally, both A-/T+ and A+/T+ groups showed significant associations between memory performance and cortical thickness of temporal regions. Despite the different pathologic terminology used for A-/T+ and A+/T+, these groups did not statistically differ on a number of clinical, cognitive and biomarker features. Although it remains unclear whether A-/T+ reflects a pathologic construct separable from Alzheimer's disease, our results provide evidence that this group typically characterized as 'non-Alzheimer's pathologic change' or 'primary age-related tauopathy' should be given increased attention, given some similarities in cognitive and biomarker characteristics to groups traditionally considered to be on the Alzheimer's continuum.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; biomarkers; primary age-related tauopathy; tau.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Zeitschr Psychiatr Psychiatr Gerichtl Med. 1907;64:146–148.
-
- Hardy J. The discovery of Alzheimer-causing mutations in the APP gene and the formulation of the “amyloid cascade hypothesis”. FEBS J. 2017;284(7):1040–1044. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Allsop D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991;12(10):383–388. - PubMed
