Evaluation of a National Quality Improvement Collaborative for Improving Cancer Screening
- PMID: 36383381
- PMCID: PMC9669819
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42354
Evaluation of a National Quality Improvement Collaborative for Improving Cancer Screening
Abstract
Importance: Cancer screening deficits during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic were found to persist into 2021. Cancer-related deaths over the next decade are projected to increase if these deficits are not addressed.
Objective: To assess whether participation in a nationwide quality improvement (QI) collaborative, Return-to-Screening, was associated with restoration of cancer screening.
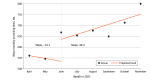
Design, setting, and participants: Accredited cancer programs electively enrolled in this QI study. Project-specific targets were established on the basis of differences in mean monthly screening test volumes (MTVs) between representative prepandemic (September 2019 and January 2020) and pandemic (September 2020 and January 2021) periods to restore prepandemic volumes and achieve a minimum of 10% increase in MTV. Local QI teams implemented evidence-based screening interventions from June to November 2021 (intervention period), iteratively adjusting interventions according to their MTVs and target. Interrupted time series analyses was used to identify the intervention effect. Data analysis was performed from January to April 2022.
Exposures: Collaborative QI support included provision of a Return-to-Screening plan-do-study-act protocol, evidence-based screening interventions, QI education, programmatic coordination, and calculation of screening deficits and targets.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was the proportion of QI projects reaching target MTV and counterfactual differences in the aggregate number of screening tests across time periods.
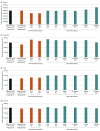
Results: Of 859 cancer screening QI projects (452 for breast cancer, 134 for colorectal cancer, 244 for lung cancer, and 29 for cervical cancer) conducted by 786 accredited cancer programs, 676 projects (79%) reached their target MTV. There were no hospital characteristics associated with increased likelihood of reaching target MTV except for disease site (lung vs breast, odds ratio, 2.8; 95% CI, 1.7 to 4.7). During the preintervention period (April to May 2021), there was a decrease in the mean MTV (slope, -13.1 tests per month; 95% CI, -23.1 to -3.2 tests per month). Interventions were associated with a significant immediate (slope, 101.0 tests per month; 95% CI, 49.1 to 153.0 tests per month) and sustained (slope, 36.3 tests per month; 95% CI, 5.3 to 67.3 tests per month) increase in MTVs relative to the preintervention trends. Additional screening tests were performed during the intervention period compared with the prepandemic period (170 748 tests), the pandemic period (210 450 tests), and the preintervention period (722 427 tests).
Conclusions and relevance: In this QI study, participation in a national Return-to-Screening collaborative with a multifaceted QI intervention was associated with improvements in cancer screening. Future collaborative QI endeavors leveraging accreditation infrastructure may help address other gaps in cancer care.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American College of Surgeons . Return to Cancer Screening PDSA quality improvement project and clinical study. Accessed October 13, 2022. https://www.facs.org/media/it2bls0g/return_to_screening_pdsa_and_clinica...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

