Harmonic radar tracking of individual melon flies, Zeugodacus cucurbitae, in Hawaii: Determining movement parameters in cage and field settings
- PMID: 36383542
- PMCID: PMC9668202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276987
Harmonic radar tracking of individual melon flies, Zeugodacus cucurbitae, in Hawaii: Determining movement parameters in cage and field settings
Abstract
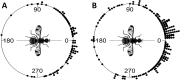
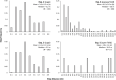
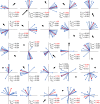
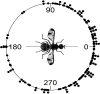
Tephritid fruit flies, such as the melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae, are major horticultural pests worldwide and pose invasion risks due primarily to international trade. Determining movement parameters for fruit flies is critical to effective surveillance and control strategies, from setting quarantine boundaries after incursions to development of agent-based models for management. While mark-release-recapture, flight mills, and visual observations have been used to study tephritid movement, none of these techniques give a full picture of fruit fly movement in nature. Tracking tagged flies offers an alternative method which has the potential to observe individual fly movements in the field, mirroring studies conducted by ecologists on larger animals. In this study, harmonic radar (HR) tags were fabricated using superelastic nitinol wire which is light (tags weighed less than 1 mg), flexible, and does not tangle. Flight tests with wild melon flies showed no obvious adverse effects of HR tag attachment. Subsequent experiments successfully tracked HR tagged flies in large field cages, a papaya field, and open parkland. Unexpectedly, a majority of tagged flies showed strong flight directional biases with these biases varying between flies, similar to what has been observed in the migratory butterfly Pieris brassicae. In field cage experiments, 30 of the 36 flies observed (83%) showed directionally biased flights while similar biases were observed in roughly half the flies tracked in a papaya field. Turning angles from both cage and field experiments were non-random and indicate a strong bias toward continued "forward" movement. At least some of the observed direction bias can be explained by wind direction with a correlation observed between collective melon fly flight directions in field cage, papaya field, and open field experiments. However, individual mean flight directions coincided with the observed wind direction for only 9 out of the 25 flies in the cage experiment and half of the flies in the papaya field, suggesting wind is unlikely to be the only factor affecting flight direction. Individual flight distances (meters per flight) differed between the field cage, papaya field, and open field experiments with longer mean step-distances observed in the open field. Data on flight directionality and step-distances determined in this study might assist in the development of more effective control and better parametrize models of pest tephritid fruit fly movement.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Ormsby MD. Establishing criteria for the management of tephritid fruit fly outbreaks. CABI Agric Biosci. 2021;2(1):1–22.
-
- Liquido NJ, McQuate GT, Hanlin MA, Suiter KA. Host plants of the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann), Version 4.0, Available at: USDA Compendium of Fruit Fly Host Information (CoFFHI) https://coffhi.cphst.org/. 2020.
-
- Liquido N, McQuate G, Birnbaum A, Hanlin M, Nakamichi K, Inskeep J, et al.. A review of recorded host plants of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)(Diptera: Tephritidae), Version 4.0. Available at USDA Compendium of Fruit Fly Host Information (CoFFHI) https://coffhi.cphst.org/. 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

