Incidence, subtypes, sex differences and trends of stroke in Taiwan
- PMID: 36383604
- PMCID: PMC9668115
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277296
Incidence, subtypes, sex differences and trends of stroke in Taiwan
Abstract
Background: Chinese populations have been reported higher incidence of all strokes and intracerebral hemorrhage. However, few large-scale studies have evaluated changes of stroke epidemiology in the 21st century.
Methods: We explored the rates of incidence of all first-ever strokes, subtypes, and 1-month case fatality by using data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database since 2004. Also, we investigated sex differences in stroke. Time-trend analysis was performed for incidence and case fatality rates of all strokes and subtypes in both sexes.
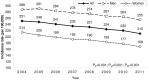
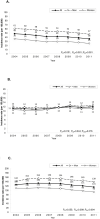
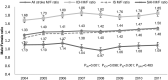
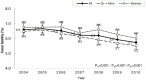
Results: The age-adjusted incidence of all strokes per 100,000 person-years decreased by 16%, from 251 (95% confidence interval [CI] 249-253) in 2004 to 210 (95% CI 209-212) in 2011 (p<0.001); it was always higher in Chinese men than in women. Among pathological subtypes, the incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage markedly decreased by 26% over the years (p<0.001), while that of ischemic stroke slightly decreased by 8%. However, when stratified by sex, the incidence of ischemic stroke decreased significantly in only women, not in men (men: p = 0.399, women: p = 0.004). Regarding the incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage, it remained unchanged. Furthermore, the rate of 1-month case fatality decreased significantly for all strokes in both sexes (p<0.001).
Conclusions: In Taiwan, the incidence rate of first-ever stroke decreased in both Chinese men and women in the early 21st century. Men had a higher incidence rate than women. Furthermore, a marked decrease was noted in the incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage, while a slight decrease was noted in that of ischemic stroke; however, the decreased incidence of ischemic stroke was significant in only women.
Copyright: © 2022 Tsai et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

