First-in-human phase Ia study of the PI3Kα inhibitor CYH33 in patients with solid tumors
- PMID: 36385120
- PMCID: PMC9669016
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34782-9
First-in-human phase Ia study of the PI3Kα inhibitor CYH33 in patients with solid tumors
Abstract
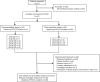
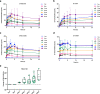
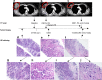
PIK3CA mutations are highly prevalent in solid tumors. Targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α is therefore an attractive strategy for treating cancers harboring PIK3CA mutations. Here, we report the results from a phase Ia, open label, dose-escalation and -expansion study (NCT03544905) of CYH33, a highly selective PI3Kα inhibitor, in advanced solid tumors. The primary outcomes were the safety, tolerability, maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of CYH33. The secondary outcomes included evaluation of pharmacokinetics, preliminary efficacy and changes in pharmacodynamic biomarkers in response to CYH33 treatment. The exploratory outcome was the relationship between the efficacy of CYH33 treatment and tumor biomarker status, including PIK3CA mutations. A total of 51 patients (19 in the dose escalation stage and 32 in the dose expansion stage) including 36 (70.6%) patients (4 in the dose escalation stage and 32 in the dose expansion stage) with PIK3CA mutations received CYH33 1-60 mg. The MTD of CYH33 was 40 mg once daily, which was also selected as the RP2D. The most common grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events were hyperglycemia, rash, platelet count decreased, peripheral edema, and fatigue. Forty-two out of 51 patients were evaluable for response, the confirmed objective response rate was 11.9% (5/42). Among 36 patients harboring PIK3CA mutations, 28 patients were evaluable for response, the confirmed objective response rate was 14.3% (4/28). In conclusion, CYH33 exhibits a manageable safety profile and preliminary anti-tumor efficacy in solid tumors harboring PIK3CA mutations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: Q.-Q.Y. and Y.-W.D. are employed by Haihe Biopharma Co., Ltd. The rest of authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decrease in phosphorylated ERK indicates the therapeutic efficacy of a clinical PI3Kα-selective inhibitor CYH33 in breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2018 Oct 1;433:273-282. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30003928
-
Alpelisib Plus Fulvestrant in PIK3CA-Altered and PIK3CA-Wild-Type Estrogen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer: A Phase 1b Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Feb 1;5(2):e184475. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4475. Epub 2019 Feb 14. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30543347 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase α-Selective Inhibition With Alpelisib (BYL719) in PIK3CA-Altered Solid Tumors: Results From the First-in-Human Study.J Clin Oncol. 2018 May 1;36(13):1291-1299. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.7107. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29401002 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I Open-Label Study to Identify a Dosing Regimen of the Pan-AKT Inhibitor AZD5363 for Evaluation in Solid Tumors and in PIK3CA-Mutated Breast and Gynecologic Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 May 1;24(9):2050-2059. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2260. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29066505 Clinical Trial.
-
Repressing MYC by targeting BET synergizes with selective inhibition of PI3Kα against B cell lymphoma.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jan 1;524:206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.022. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 34688842
Cited by
-
Intact regulation of G1/S transition renders esophageal squamous cell carcinoma sensitive to PI3Kα inhibitors.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Apr 12;8(1):153. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01359-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37041169 Free PMC article.
-
In silico discovery of a novel potential allosteric PI3Kα inhibitor incorporating 2-oxopropyl urea targeting head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Chem. 2025 Feb 28;19(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01420-6. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 40022235 Free PMC article.
-
A Paradoxical AKT: Exploring the Promise and Challenges of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Targeted Therapies.J Cancer Immunol (Wilmington). 2024;6(3):92-99. doi: 10.33696/cancerimmunol.6.089. J Cancer Immunol (Wilmington). 2024. PMID: 39381117 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting PI3K family with small-molecule inhibitors in cancer therapy: current clinical status and future directions.Mol Cancer. 2024 Aug 10;23(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02072-1. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39127670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic activation of PI K3 CA in cancers: Emerging targeted therapies in precision oncology.Genes Dis. 2024 Sep 10;12(2):101430. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101430. eCollection 2025 Mar. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39717717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

