Identification of texture MRI brain abnormalities on first-episode psychosis and clinical high-risk subjects using explainable artificial intelligence
- PMID: 36385133
- PMCID: PMC9668814
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02242-z
Identification of texture MRI brain abnormalities on first-episode psychosis and clinical high-risk subjects using explainable artificial intelligence
Abstract
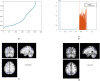
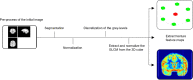
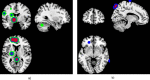
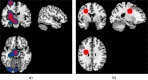
Structural MRI studies in first-episode psychosis and the clinical high-risk state have consistently shown volumetric abnormalities. Aim of the present study was to introduce radiomics texture features in identification of psychosis. Radiomics texture features describe the interrelationship between voxel intensities across multiple spatial scales capturing the hidden information of underlying disease dynamics in addition to volumetric changes. Structural MR images were acquired from 77 first-episode psychosis (FEP) patients, 58 clinical high-risk subjects with no later transition to psychosis (CHR_NT), 15 clinical high-risk subjects with later transition (CHR_T), and 44 healthy controls (HC). Radiomics texture features were extracted from non-segmented images, and two-classification schemas were performed for the identification of FEP vs. HC and FEP vs. CHR_NT. The group of CHR_T was used as external validation in both schemas. The classification of a subject's clinical status was predicted by importing separately (a) the difference of entropy feature map and (b) the contrast feature map, resulting in classification balanced accuracy above 72% in both analyses. The proposed framework enhances the classification decision for FEP, CHR_NT, and HC subjects, verifies diagnosis-relevant features and may potentially contribute to identification of structural biomarkers for psychosis, beyond and above volumetric brain changes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Borgwardt SJ, Riecher-Rössler A, Dazzan P, Chitnis X, Aston J, Drewe M, et al. Regional gray matter volume abnormalities in the at risk mental state. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:1148–56. - PubMed
-
- Chopra S, Fornito A, Francey SM, O’Donoghue B, Cropley V, Nelson B, et al. Differentiating the effect of antipsychotic medication and illness on brain volume reductions in first-episode psychosis: a Longitudinal, Randomised, Triple-blind, Placebo-controlled MRI Study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021;46:1494–501. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fusar-Poli P, Deste G, Smieskova R, Barlati S, Yung AR, Howes O, et al. Cognitive functioning in prodromal psychosis: a meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:562–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

