Effect of femoral stem surface coating on clinical and radiographic outcomes of cementless primary total hip arthroplasty: a patient-matched retrospective study
- PMID: 36385185
- PMCID: PMC9668389
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-022-05629-1
Effect of femoral stem surface coating on clinical and radiographic outcomes of cementless primary total hip arthroplasty: a patient-matched retrospective study
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to determine whether changing the stem coating grants superior outcomes at a minimum follow-up of five years.
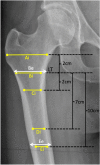
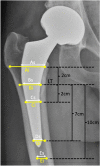
Methods: Retrospective review of a consecutive series of primary total hip arthroplasties (THAs) operated by direct anterior approach between 01/01/2013 and 31/12/2014. Two stems were compared, which were identical except for their surface coating; "the Original stem" was fully coated with hydroxyapatite (HA), while "the ProxCoat stem" was proximally coated with plasma-sprayed titanium and HA. Matching was performed. Clinical assessment included modified Harris hip score (mHHS), Oxford hip score (OHS), and forgotten joint score (FJS). Radiographic assessment evaluated alignment, subsidence, pedestal formation, heterotopic ossification, radiolucent lines ≥ 2 mm, spot welds, cortical hypertrophy, and osteolysis.
Results: 232 hips received the Original stem and 167 the ProxCoat stem, from which respectively five hips (2.2%) and no hips (0%) underwent revision. Matching identified two groups of 91 patients, with comparable patient demographics. At > five years follow-up, there were no differences in OHS (16 ± 6 vs 15 ± 5; p = 0.075) nor FJS (81 ± 26 vs 84 ± 22; p = 0.521), but there were differences in mHHS (89 ± 15 vs 92 ± 12; p = 0.042). There were no differences in alignment, subsidence, pedestal formation, heterotopic ossification, cortical hypertrophy, and osteolysis. There were differences in prevalence of proximal radiolucent lines (12% vs 0%; p < 0.001) and distal spot welds (24% vs 54%; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: At a minimum follow-up of five years, this study on matched patients undergoing primary THA found that ProxCoat stems results in significantly fewer radiolucent lines, more spot welds, and less revisions than Original stems, thus suggesting better bone ingrowth.
Keywords: Cementless stem; Clinical outcomes; Radiographic outcomes; Surface coating; Total hip arthroplasty; Total hip replacement.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to SICOT aisbl.
Conflict of interest statement
MRVG, SRP, MS, and JS have nothing to declare. FL declares royalties from Medacta.
Figures

Similar articles
-
No differences in clinical and radiographic outcomes between standard versus high offset collared stems for primary total hip arthroplasty at five years follow-up.Int Orthop. 2024 Oct;48(10):2525-2533. doi: 10.1007/s00264-024-06264-8. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39112838
-
Satisfactory clinical and radiographic outcomes following revision total hip arthroplasty by direct anterior approach using primary femoral stems at 2-8 years of follow-up.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Oct;143(10):6393-6402. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-04838-6. Epub 2023 Mar 19. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 36935414
-
A randomized trial of hydroxyapatite coated prostheses in total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999 Sep;(366):120-32. doi: 10.1097/00003086-199909000-00016. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. PMID: 10627726 Clinical Trial.
-
Mid-term outcome of total hip arthroplasty using a short stem.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016 Dec;24(3):323-327. doi: 10.1177/1602400310. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016. PMID: 28031499
-
High wear rates and extensive osteolysis in 3 types of uncemented total hip arthroplasty: a review of the PCA, the Harris Galante and the Profile/Tri-Lock Plus arthroplasties with a minimum of 12 years median follow-up in 96 hips.Acta Orthop. 2006 Aug;77(4):575-84. doi: 10.1080/17453670610012638. Acta Orthop. 2006. PMID: 16929433 Review.
Cited by
-
No differences in clinical and radiographic outcomes between standard versus high offset collared stems for primary total hip arthroplasty at five years follow-up.Int Orthop. 2024 Oct;48(10):2525-2533. doi: 10.1007/s00264-024-06264-8. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39112838
-
Improved radiographic outcomes and decreased complications rate on the femoral side can be achieved by a novel designed whole-process robotic assisted hip system for total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial.J Robot Surg. 2024 Feb 16;18(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-01835-8. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 38365906 Clinical Trial.
-
High subsidence rate in primary total hip arthroplasty with a taper wedge stem featuring a three-dimensionally printed porous structure.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025 Mar 14;145(1):188. doi: 10.1007/s00402-025-05809-9. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025. PMID: 40085230
-
Over ten-year follow-up results of a prospective and consecutive series of primary total hip arthroplasty with an original cementless total hip prosthesis.Int Orthop. 2024 Apr;48(4):945-954. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-06071-7. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38153431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medium-term outcome of the Libra® cemented versus cementless stems in primary dual mobility total hip arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Aug 21;24(1):663. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06799-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37599372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahun-Mairal B, Agullo-Ferre JL, Rodriguez-Perez D, Garreta-Catala I, Tramunt-Monsonet C, Videla S, Coscujuela-Maña A. Primary total hip arthroplasty with a fully porous-coated uncemented stem: up to twenty-eight years. Retrospective cohort study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022;32:91–97. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-02940-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hailer NP, Lazarinis S, Mäkelä KT, Eskelinen A, Fenstad AM, Hallan G, Havelin L, Overgaard S, Pedersen AB, Mehnert F, Kärrholm J. Hydroxyapatite coating does not improve uncemented stem survival after total hip arthroplasty! Acta Orthop. 2015;86:18–25. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2014.957088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

