Anti-inflammatory effect of green photobiomodulation in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 36385209
- PMCID: PMC9668707
- DOI: 10.1007/s10103-022-03654-5
Anti-inflammatory effect of green photobiomodulation in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
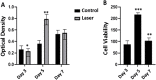
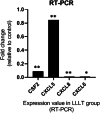
Photo biomodulation (PBM) as a non-invasive and safe treatment has been demonstrated the anti-inflammatory potential in a variety of cell types, including stem cells. However, further investigations using different laser parameters combined with more accurate methods such as quantitative measurement of inflammatory gene expression at the mRNA level are still necessary. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of 532 nm green laser on cell proliferation as well as expression of inflammatory genes in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hADMSCs) using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) technique and confirmatory RT-PCR. hADMSCs were cultured in DMEM low glocuse medium with 10% fetal bovine serum until the fourth passage. Cultured cells were divided in two groups: control group (no laser irradiation) and laser group, irradiated with 532 nm laser at 44 m J/cm2 with an output power of 50 mW and a density of 6 mW/cm2, every other day, 7 s each time. The cell viability was assessed using MTT assay 24 h after each irradiation on days 3, 5, and 7 after cell seeding, followed by performing RNA-seq and RT-PCR. The MTT assay showed that PBM increased cell proliferation on day 5 after irradiation compared to day 3 and decreased on day 7 compared to day 5. In addition, gene expression analysis in hADMSCs using RNA-seq revealed down-regulation of inflammatory genes including CSF2, CXCL2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and CCL2, 7. These results indicate that 532 nm PBM with the parameters used in this study has a time-dependent effect on hADMSCs proliferation as well as anti-inflammatory potential.
Keywords: Inflammation; Low-level light therapy; Mesenchymal stem cells; RNA; Sequence analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag London Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Photobiomodulation effect on the proliferation of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Jun;34(4):677-683. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2642-2. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30284088
-
Label-free and real-time assessment of 660 nm red light photobiomodulation induced molecular alterations in human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells using micro Raman spectroscopy.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025 Mar 15;329:125552. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.125552. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025. PMID: 39647267
-
Near-infrared 940-nm diode laser photobiomodulation of inflamed periodontal ligament stem cells.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Feb;37(1):449-459. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03282-5. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 33740139
-
Effect of Photobiomodulation on Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Photomed Laser Surg. 2016 Nov;34(11):533-542. doi: 10.1089/pho.2015.4029. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Photomed Laser Surg. 2016. PMID: 27070113 Review.
-
Effect of low-level laser-treated mesenchymal stem cells on myocardial infarction.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Sep;32(7):1637-1646. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2271-1. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28681086 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of quantum hyperlight technology in photobiomodulation on stem cells: an experimental in vitro study.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Feb 15;40(1):96. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04358-2. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39954213 Free PMC article.
-
Light assisted modulation of stem cell function and secretome production: a systematic review on current status and new avenues for regenerative medicine.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Feb 12;40(1):83. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04339-5. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39934459 Free PMC article.
-
Review on the molecular mechanisms of low-level laser therapy: gene expression and signaling pathways.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Mar 25;40(1):160. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04393-z. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40131476 Review.
-
Enhancing Osteoblast Differentiation from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Using Hydrogels and Photobiomodulation: Overcoming In Vitro Limitations for Osteoporosis Treatment.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 25;46(7):6346-6365. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070379. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao Q, Ren H, Han Z. Mesenchymal stem cells: immunomodulatory capability and clinical potential in immune diseases. J Cell Immunotherapy. 2016;2(1):3–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jocit.2014.12.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

