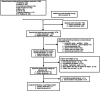
Influencing factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36385501
- PMCID: PMC10088840
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.14017
Influencing factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis
Abstract
This study aims to systematically review and identify the related influencing factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs)in diabetic patients. We searched PUBMED, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, China Biology Medicine (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wan Fang and VIP databases to identify eligible studies published before March 31, 2022 to collect case-control studies or cohort studies on the related influencing factors for the recurrence of DFUs. Two reviewers independently screened the literature, and extracted data. Also, they assessed the risk of bias of the included studies using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. A meta-analysis was performed using RevMan5.4.1 software. 20 studies were included; 4238 patients were enrolled, in which 1567 were in the DFU recurrence group and 2671 were in the non-recurrent DFU group. Risk factors for the recurrence of DFUs included diabetic peripheral neuropathy (odds ratio [OR] = 4.05, 95% CI, 2.50-6.58, P < 0.00001), peripheral vascular disease (OR = 3.94, 95% CI, 2.65-5.84, P < 0.00001), poor blood glucose control (OR = 3.27, 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.79-3.84, P < 0.00001), plantar ulcer (OR = 3.66, 95% CI, 2.06-6.50, P < 0.00001), osteomyelitis (OR = 7.17, 95% CI, 2.29-22.47, P = 0.0007), smoking (OR = 1.98, 95% CI, 1.65-2.38, P < 0.00001), history of amputation (OR = 11.96, 95%CI, 4.60-31.14, P < 00001), multidrug-resistant bacterial infection (OR = 3.61, 95%CI, 3.13-4.17, P < 0.00001), callus (OR = 5.70, 95%CI, 1.36-23.89, P = 0.02), previous diabetic foot ulcer (OR = 4.10, 95% CI, 2.58-6.50, P < 0.00001), duration of previous diabetic foot ulcer >60d (OR = 1.02, 95% CI, 1.00-1.03, P = 0.004), history of vascular intervention (OR = 3.20, 95% CI, 2.13-4.81, P < 0.00001) and Wagner grade III/IV (OR = 4.40, 95% CI, 2.21-8.78, P < 0.0001). However, no significant differences were found in age, duration of diabetes, body mass index, total cholesterol or foot deformity. Recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers is affected by a variety of factors. Thus, we should focus on high-risk groups and take targeted interventions as soon as possible to reduce the recurrence rate of DFUs, because of the limited quality and quantity of the included studies, more rigorous studies with adequate sample sizes are needed to verify the conclusion.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer; meta-analysis; recurrence; risk factor.
© 2022 The Authors. International Wound Journal published by Medicalhelplines.com Inc (3M) and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

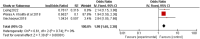
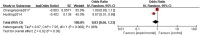






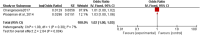
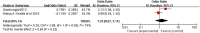
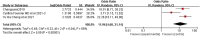
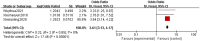
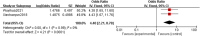
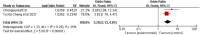

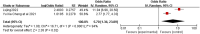
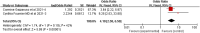
References
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88‐98. - PubMed
-
- van Netten JJ, Bus SA, Apelqvist J, et al. Definitions and criteria for diabetic foot disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(Suppl 1):e3268. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM, Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367‐2375. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Wang X, Xia L, et al. A cohort study of diabetic patients and diabetic foot ulceration patients in China. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(2):222‐230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

