Efficacy, safety, and molecular response predictors of oral ixazomib and short-course rituximab in untreated iNHL
- PMID: 36385536
- PMCID: PMC9984960
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008628
Efficacy, safety, and molecular response predictors of oral ixazomib and short-course rituximab in untreated iNHL
Abstract
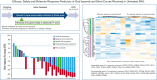
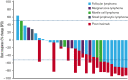
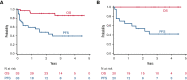
Patients with indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) generally require treatment but experience normal survival, emphasizing the need for simpler, safer therapies. Proteasome inhibitors target aberrant signaling pathways within iNHL and have manageable toxicities. We evaluated the oral proteasome inhibitor ixazomib as initial monotherapy, and combined with rituximab, for first-line treatment of iNHL. Treatment-naïve patients with iNHL needing therapy received oral ixazomib 4 mg weekly until progressive disease or unacceptable adverse events. A 4-week course of rituximab was added during month 7. The primary end point was overall response rate (ORR) during the ixazomib monotherapy window. Correlations included gene expression profiling and response to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination. Thirty-three patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) (n = 20), marginal zone lymphoma (n = 7), and other iNHL were treated with a median follow-up of 30.3 months. During the 6-month ixazomib window, the ORR was 24%, including 35% in FL. The best ORR over the entire study period was 52% overall and 65% in FL; complete response was achieved in 33% and 45%, respectively. The median duration of response was 25.8 months (range, 0-49.7), and the 24-month progression-free and overall survival rates were 51% (95% confidence interval [CI], 32-67) and 91% (95% CI, 74-97), respectively. Ixazomib was well tolerated. Baseline downregulation of proteasome genes, PSMB9 (P = .03) and PSMB8 (P = .007), were associated with response. All evaluated patients generated anti-S antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, with a median of 254.9 binding arbitrary unit per mL. Ixazomib demonstrated efficacy alone and with short-course rituximab in untreated iNHL while exhibiting favorable toxicity, convenience, and retention of the B-cell immune response. This trial is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT02339922.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.A.G. received research funding from TG Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, GSK, and MorphoSys. R.C.L. serves as a consultant for MorphoSys; received research funding from TG Therapeutics, SeaGen, RAPT, Juno Therapeutics, Incyte, Bayer, Cyteir, and Genentech. C.S.U. serves as a consultant for Atara, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, ACDT, Epizyme, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, and BeiGene. A.J.C. received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Harpoon, and Nektar; serves as a consultant for Secura Bio, GSK, and Cellectar; and serves as a consultant and received research funding from Sanofi Aventis, AbbVie, and Janssen. S.D.S. serves as a consultant for Millenium/Takeda, Karyopharm, KITE pharm, Incyte, and ADC Therapeutics; received research funding from Portola Pharmaceuticals, Incyte Corporation, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, Genetech, Acerta Pharma BV, De Novo Biopharma, and Bayer; received research funding from Ignyta (spouse), Bristol Myers Squibb (spouse), Ayala (spouse); and serves as a consultant and received research funding from BeiGene and AstraZeneca. M.S. serves as a consultant for AbbVie, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Sound Biologics, Pharmacyclics, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, MorphoSys, TG Therapeutics, Innate Pharma, Kite Pharma, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Epizyme, Eli Lilly, Adaptimmune, Mustang Bio, and Atara Biotherapeutics: Consultancy; and received research funding from Mustang Bio, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Gilead, Genentech, AbbVie, TG Therapeutics, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Sunesis, Atara Biotherapeutics, and GenMab. E.N.L. serves as a consultant and received research funding from Janssen; and received research funding from BMS, Genentech, and GSK. A.K.G. received research funding from Agios, Takeda, IGM Biosciences, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Teva; serves as a consultant for and received Honoraria from BeiGene, Servier, ADC Therapeutics, Kite, Acrotech, Karyopharm, Epizyme, Nurix Inc, and Cellectar; received Honoraria from MorphoSys and Incyte; serves as a consultant for, received research funding and Honoraria from Merck, SeaGen, Genetech, Gilead, I-Mab Biopharma, and Janssen.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lenalidomide, rituximab (R2), and ixazomib for frontline treatment of high risk follicular and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2024 Jun;65(6):768-773. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2024.2325636. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Leuk Lymphoma. 2024. PMID: 38456694 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of ibrutinib in combination with rituximab and lenalidomide in previously untreated follicular and marginal zone lymphoma: An open label, phase 2 study.Cancer. 2024 Mar 15;130(6):876-885. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35114. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37985359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
DYNAMO: A Phase II Study of Duvelisib (IPI-145) in Patients With Refractory Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr 10;37(11):912-922. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00915. Epub 2019 Feb 11. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30742566 Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Novel Therapies for Follicular Lymphoma and Other Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021 Oct 25;22(12):111. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00909-1. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34694508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteasome inhibition overcomes resistance to targeted therapies in B-cell malignancy models and in an index patient.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 23;16(1):555. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07884-7. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40701968 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Nov 9;18(1):20230834. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0834. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 38025532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nastoupil LJ, Sinha R, Byrtek M, et al. Outcomes following watchful waiting for stage II-IV follicular lymphoma patients in the modern era. Br J Haematol. 2016;172(5):724–734. - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Imrie K, Solal-Celigny P, et al. Phase III study of R-CVP compared with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone alone in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(28):4579–4586. - PubMed
-
- Brice P, Bastion Y, Lepage E, et al. Comparison in low-tumor-burden follicular lymphomas between an initial no-treatment policy, prednimustine, or interferon alfa: a randomized study from the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes Folliculaires. Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(3):1110–1117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

