Preparation and Characterization of Aprepitant Solid Dispersion with HPMCAS-LF
- PMID: 36385804
- PMCID: PMC9647728
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04021
Preparation and Characterization of Aprepitant Solid Dispersion with HPMCAS-LF
Abstract
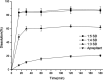
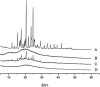
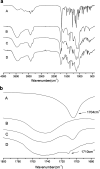
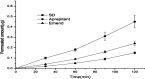
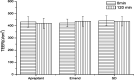
This study focused on improving the physicochemical characteristics of aprepitant with poor water solubility by preparing solid dispersion (SD). To prepare the SD with HPMCAS-LF, the solvent evaporation method was applied. Based on dissolution analysis, the dissolution rate of SD increased by five times compared with aprepitant. In addition, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) results suggested the presence of amorphous-form aprepitant inside SD. According to Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, intermolecular hydrogen bonds were detected between polymer and aprepitant. The Caco-2 cell experiment proved that SD did not lower the transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) values but improved the permeation amount of aprepitant. Additionally, the SD of aprepitant displayed excellent stability.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design and Characterization of Phosphatidylcholine-Based Solid Dispersions of Aprepitant for Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Apr 29;12(5):407. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050407. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32365589 Free PMC article.
-
Amorphous solid dispersion preparation via coprecipitation improves the dissolution, oral bioavailability, and intestinal health enhancement properties of magnolol.Poult Sci. 2023 Jun;102(6):102676. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102676. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37104903 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Study of Aprepitant Solid Dispersions with Soluplus®.Molecules. 2015 Jun 19;20(6):11345-56. doi: 10.3390/molecules200611345. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26102068 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative physicochemical characterization of phospholipids complex of puerarin formulated by conventional and supercritical methods.Pharm Res. 2008 Mar;25(3):563-77. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9418-x. Epub 2007 Sep 8. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17828444
-
[Effect of HPMCAS/curcumin amorphous solid dispersion in enhancing dissolution and chemical stability of curcumin].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;44(15):3305-3311. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190516.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602887 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Advances in the research and application of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024 Feb 15;25(2):91-105. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300455. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024. PMID: 38303494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formulating abiraterone acetate-HPMCAS-based amorphous solid dispersions: insights into in vitro and biorelevant dissolution assessments and pharmacokinetic evaluations.RSC Adv. 2024 Dec 5;14(52):38492-38505. doi: 10.1039/d4ra08163c. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39640520 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Tetrandrine Nanocrystals to Improve Bioavailability.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025;22(5):648-657. doi: 10.2174/0115672018341709241121092617. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 39722488
-
Emerging Applications of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Acetate Succinate: Different Aspects in Drug Delivery and Its Commercial Potential.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Sep 15;24(7):188. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02645-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 37715004 Review.
-
Aprepitant-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: a novel approach to enhance oral bioavailability.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025 May 15;16:652-663. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.16.50. eCollection 2025. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40438268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sorbera L. A.; Castañer J.; Bayés M.; Silvestre J. Aprepitant and L-758298. Drugs Future 2002, 27, 211–222. 10.1358/dof.2002.027.03.661047. - DOI
-
- Nama S.; Chandu B. R.; Awen B. Z.; Khagga M. Development and Validation of a New RP-HPLC Method for the Determination of Aprepitant in Solid Dosage Forms. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 491–497. 10.4314/tjpr.v10i4.15. - DOI
-
- Cocquyt V.; Van Belle S.; Belle S. V.; Reinhardt R. R.; Decramer M.; O’Brien M.; O’Brien M.; Schellens J.; Schelle J. H.; Borms M.; Verbeke L.; Verbeke L.; Van A. F.; Van Aelst F.; De S. M.; De Smet M.; Carides A. D.; Carides A.; Eldridge K.; Eldridge K.; Gretz B. J. Comparison of L-758,298, a prodrug for the selective neurokinin-1 antagonist, L-754,030, with ondansetron for the prevention of cisplatin-induced emesis. Eur. J. Cancer. 2001, 37, 835–842. 10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00416-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu Y.; Loper A.; Landis E.; Hettrick L.; Novak L.; Lynn K.; Chen C.; Thompson K.; Higgins R.; Batra U.; Shelukar S.; Kwei G.; Storey D. The role of biopharmaceutics in the development of a clinical nanoparticle formulation of MK-0869: a Beagle dog model predicts improved bioavailability and diminished food effect on absorption in human. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 285, 135–146. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.08.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

