Deciphering the role of DOCK8 in tumorigenesis by regulating immunity and the application of nanotechnology in DOCK8 deficiency therapy
- PMID: 36386145
- PMCID: PMC9664064
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1065029
Deciphering the role of DOCK8 in tumorigenesis by regulating immunity and the application of nanotechnology in DOCK8 deficiency therapy
Abstract
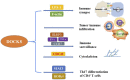
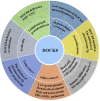
The dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) immunodeficiency syndrome is a severe immune disorder and characterized by serum IgE levels elevation, fungal and viral infections, dermatitis and food allergies. It was well known that DOCK8 is crucial for the survival and function of multiple immune related cells. However, the critical role of DOCK8 on tumorigenesis through regulating immunity is poorly investigated. Accumulating evidences indicated that DOCK8 could affect tumorigenesis by regulating the immunity through immune cells, including NK cells, T cells, B cells and dendritic cells. Here, we summarized and discussed the critical role of DOCK8 in cytoskeleton reconstruction, CD4+ T cell differentiation, immune synaptic formation, tumor immune infiltration, tumor immune surveillance and tumorigenesis. Furthermore, the potential roles of nanotechnology in improving the hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-based therapy for DOCK8 deficiency diseases are also highlighted and discussed.
Keywords: Cdc42; NK cells; cytoskeleton; dedicator of cytokinesis 8; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; immunity; nanotechnology; tumor.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Cao, Dai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DOCK8 deficiency: Insights into pathophysiology, clinical features and management.Clin Immunol. 2017 Aug;181:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28625885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dedicator of cytokinesis 8-deficient CD4+ T cells are biased to a TH2 effector fate at the expense of TH1 and TH17 cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Mar;139(3):933-949. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Aug 20. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27554822 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, immunological features and follow up of 20 patients with dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) deficiency.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2020 Jul;31(5):515-527. doi: 10.1111/pai.13236. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32108967 Free PMC article.
-
Defective actin accumulation impairs human natural killer cell function in patients with dedicator of cytokinesis 8 deficiency.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Mar;131(3):840-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.12.1568. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23380217 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into immunity from clinical and basic science studies of DOCK8 immunodeficiency syndrome.Immunol Rev. 2019 Jan;287(1):9-19. doi: 10.1111/imr.12723. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis and Regulatory Mechanisms of Platelet-Related Genes in Patients with Ischemic Stroke.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jan 4;44(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01433-6. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38175286 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Copy Number Alterations and Copy Neutral Loss of Heterozygosity in Adult Ph-Negative Acute B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Focus on the Genes Involved.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17602. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417602. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Khatib S., Keles S., Garcia-Lloret M., Karakoc-Aydiner E., Reisli I., Artac H., et al. (2009). Defects along the T(H)17 differentiation pathway underlie genetically distinct forms of the hyper IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 124 (2), 342–345. 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

