Rituximab for the treatment of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36386239
- PMCID: PMC9650441
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1019915
Rituximab for the treatment of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a common pulmonary disease often associated with significant morbidity and mortality in patients with connective tissue diseases (CTD). Currently, no gold-standard therapies are available for CTD-ILD. Recently, several studies have proposed that rituximab (RTX) may be effective for the treatment of CTD-ILD. Objectives: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of RTX for the treatment of CTD-ILD. Methods: Studies were selected from PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, up to 20 July 2022. Improvement and stable rates were extracted as the main outcomes and pooled using the weighted mean proportion with fixed or random-effects models, in case of significant heterogeneity (I 2 > 50%). Safety analysis was performed based on the adverse events reported in all of the studies. Results: Thirteen studies (312 patients) were included in the meta-analysis. The follow-up durations ranged from 6 to 36 months. The pooled improvement rate was 35.0% (95% CI: 0.277-0.442), while the pooled stable rate was 59.2% (95% CI: 0.534-0.656). Anti-synthetase syndrome associated with ILD [ASS-ILD, 48.1% (95% CI, 0.373-0.620)] and idiopathic inflammatory myopathies associated with ILD [IIM-ILD, non-ASS, 47.4% (95% CI, 0.266-0.846)] had higher improvement rates than the other types. A total of 106 adverse events associated with RTX or progressive ILD were reported among the 318 patients, 55.7% of which were mild. Among 19 deaths, 17 were due to ILD progression, one to severe pulmonary arterial hypertension, and one to Pneumocystis jirovecii infection. Conclusion: RTX, which exhibits a satisfactory safety profile, is an effective treatment option for CTD-ILD, even in patients who fail to respond to other therapies. Further randomized trials are needed to assess the efficacy of rituximab compared to other treatments for CTD-ILD. Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, identifier (CRD42022363403).
Keywords: connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease; efficacy; meta-analysis; rituximab; safety.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Wang and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
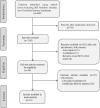
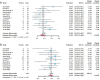
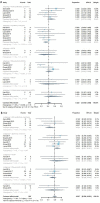
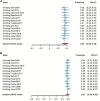
References
-
- Akiyama M., Kaneko Y., Yamaoka K., Kondo H., Takeuchi T. (2016). Association of disease activity with acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease during tocilizumab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective, case-control study. Rheumatol. Int. 36 (6), 881–889. 10.1007/s00296-016-3478-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Cardiel M. H. (1989). Comparison between 3 diagnostic criteria for mixed connective tissue disease. Study of 593 patients. J. Rheumatol. 16 (3), 328–334. - PubMed
-
- Allenbach Y., Guiguet M., Rigolet A., Marie I., Hachulla E., Drouot L., et al. (2015). Efficacy of rituximab in refractory inflammatory myopathies associated with anti- synthetase auto-antibodies: An open-label, phase II trial. PloS one 10 (11), e0133702. 10.1371/journal.pone.0133702 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

