Breast cancer liver metastasis: Pathogenesis and clinical implications
- PMID: 36387238
- PMCID: PMC9641291
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1043771
Breast cancer liver metastasis: Pathogenesis and clinical implications
Abstract
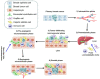
Breast cancer is the most common malignant disease in female patients worldwide and can spread to almost every place in the human body, most frequently metastasizing to lymph nodes, bones, lungs, liver and brain. The liver is a common metastatic location for solid cancers as a whole, and it is also the third most common metastatic site for breast cancer. Breast cancer liver metastasis (BCLM) is a complex process. Although the hepatic microenvironment and liver sinusoidal structure are crucial factors for the initial arrest of breast cancer and progression within the liver, the biological basis of BCLM remains to be elucidated. Importantly, further understanding of the interaction between breast cancer cells and hepatic microenvironment in the liver metastasis of breast cancer will suggest ways for the development of effective therapy and prevention strategies for BCLM. In this review, we provide an overview of the recent advances in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the hepatic microenvironment in BCLM formation and discuss current systemic therapies for treating patients with BCLM as well as potential therapeutic development based on the liver microenvironment-associated signaling proteins governing BCLM.
Keywords: breast cancer; clinical implications; hepatic microenvironment; liver metastasis; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Mohan, Wei, Seki, Liu, Basho, Giuliano, Zhao and Cui.
Conflict of interest statement
Author RB has a consulting role for Navartis, Biotheranostics, AstraZeneca, Seattle Genetics and Gilead Inc. She is the honoraria of MJH Healthcare, WebMD, and AstraZeneca, and also a speaker for Eli Lilly. She is supported by the research fundings from Merck, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, Pfizer, and Eli Lilly. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Atalay G, Biganzoli L, Renard F, Paridaens R, Cufer T, Coleman R, et al. . Clinical outcome of breast cancer patients with liver metastases alone in the anthracycline-taxane era: a retrospective analysis of two prospective, randomized metastatic breast cancer trials. Eur J Cancer. (2003) 39(17):2439–49. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(03)00601-4 - DOI - PubMed

