Research trends and hotspots in the relationship between outdoor activities and myopia: A bibliometric analysis based on the web of science database from 2006 to 2021
- PMID: 36388306
- PMCID: PMC9644123
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1047116
Research trends and hotspots in the relationship between outdoor activities and myopia: A bibliometric analysis based on the web of science database from 2006 to 2021
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to explore the current status, hotspots, and emerging research trends regarding the relationship between outdoor activities and myopia.
Methods: Publications on the relationship between outdoor activities and myopia from 2006 to 2021 were collected from the Web of Science Core Collection database. CiteSpace (version 6.1.R2) was used to performed a bibliometric analysis, and R software (version 4.1.0) was used to visualize the trends and hot map of publications.
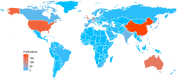
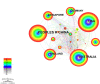
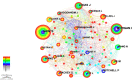
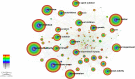
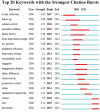
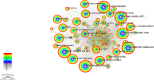
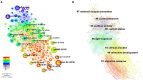
Results: A total of 640 publications were collected and analyzed in the present study. China was the major contributor (n = 204), followed by the United States of America (n = 181) and Australia (n = 137). The United States of America had the most extensive foreign cooperation (centrality = 0.25), followed by Australia (centrality = 0.20). The National University of Singapore contributed the largest number of publications (n = 48), followed by Sun Yat-Sen University (n = 41) and the Australian National University (n = 41). Among institutions, Cardiff University in the United Kingdom had the most extensive foreign cooperation (centrality = 0.12), followed by the National University of Singapore (centrality = 0.11). Saw S from Singapore had the largest number of publications (n = 39), followed by Morgan I from Australia (n = 27) and Jonas J from Germany (n = 23). Investigative ophthalmology & visual science is the most important journal to study the relationship between outdoor activities and myopia. "Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050" published by Holden BA was the most cited paper in this field with 177 citations. Co-occurrence and burst analyses of keywords showed that research trends and hotspots in this field focused mainly on "risk," "prevention" and "school".
Conclusions: The influence of outdoor activities on myopia remains a concern. In the future, deeper cooperation between countries or institutions is required to explore the effects of outdoor activities on myopia. Outdoor activities for the prevention of myopia and reduction of the risk of myopia among school students may be the focus of future research.
Keywords: CiteSpace; bibliometrics; data visualization; myopia; outdoor activities.
Copyright © 2022 Mu, Zhong, Zeng, Fan, Jiang, Liu, Shuai, Chen and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Global Tendency and Frontiers of Research on Myopia From 1900 to 2020: A Bibliometrics Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 10;10:846601. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.846601. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35359777 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspots of COVID-19 impact on sexual function: A bibliometric analysis based on Web of Science.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 19;10:976582. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.976582. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36062132 Free PMC article.
-
The knowledge structure and research trends between light and myopia: A bibliometric analysis from 1981 to 2024.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 17;103(20):e38157. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038157. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38758893 Free PMC article.
-
[Research hot spots and trends of keratoconus in China: a bibliometric analysis].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 11;60(2):156-167. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112142-20231009-00126. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38296321 Review. Chinese.
-
The applications of anterior segment optical coherence tomography in glaucoma: a 20-year bibliometric analysis.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 28;12:e18611. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18611. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39619196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and temporal dynamics analysis of neural circuit from 2002 to 2022: A bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 14;10(2):e24649. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24649. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38298625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Rapid Progression of Myopia: Topical Atropine 0.05% and MF60 Contact Lenses.Vision (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;8(1):3. doi: 10.3390/vision8010003. Vision (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391084 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of myopia-related behaviors among Chinese school-aged children and associations with parental awareness of myopia control: a population-based, cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2025 Feb 18;13:1520977. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1520977. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40041188 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles in gynecologic cancers: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 8;14:1465987. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1465987. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39845315 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of environments on school myopia by spatial analysis techniques in Wuhan.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 2;14(1):29941. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81270-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39623021 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

