Surfactin secreted by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01 is required to combat Streptomyces scabies causing potato common scab
- PMID: 36388520
- PMCID: PMC9664162
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.998707
Surfactin secreted by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01 is required to combat Streptomyces scabies causing potato common scab
Abstract
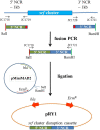
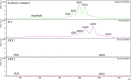
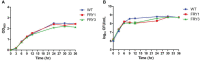
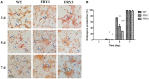
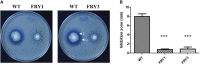
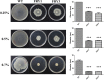
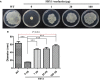
Potato common scab, which is mainly caused by the bacterium Streptomyces scabies, occurs in key potato growing regions worldwide. It causes necrotic or corky symptoms on potato tubers and decreases the economic value of potato. At present, there is no recommended chemical or biological control for combating potato common scab in Taiwan. It can only reduce the occurrence by cultivation control, but the efficacy is limited. Previously we found that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01 could control potato common scab in pot assay and in the field. The potential anti-S. scabies mechanism was associated with surfactin secretion, but further molecular dissection was not conducted. Thus, in this study we aimed to determine whether surfactin is the main compound active against S. scabies by knocking out the srf gene cluster in Ba01. The cloning plasmid pRY1 was transformed to Ba01 by electroporation for in-frame deletion. Two independent Δsrf mutants were obtained and confirmed by specific primers and mass spectrometry. The swarming ability and S. scabies inhibition was significantly decreased (P<0.001) in Δsrf mutants. The swarming ability of Δsrf mutants could be restored by the addition of surfactin. Furthermore, we found that Ba01 formed wrinkled biofilm in MSgg liquid medium, while Δsrf mutants formed biofilm abnormally. Furthermore, the α-amylase, protease and phosphate-solubilizing ability of Δsrf mutants was decreased, and the mutants could not inhibit the growth and sporulation of S. scabies on potato tuber slices. In conclusion, srf gene cluster of B. amyloliquefaciens Ba01 is responsible for the secretion of surfactin and inhibition of S. scabies.
Keywords: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Streptomyces scabies; Surfactin; potato common scab; srf gene cluster.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Chen, Lin, Tsai, Yang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Biological control of potato common scab by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 26;13(4):e0196520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196520. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29698535 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Streptomyces scabies Causing Potato Scab by Various Detection Techniques, Its Pathogenicity and Determination of Host-Disease Resistance in Potato Germplasm.Pathogens. 2020 Sep 17;9(9):760. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090760. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32957549 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of an endophytic bacteria Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 3-5 as biocontrol agent against potato scab.Microb Pathog. 2022 Feb;163:105382. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105382. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 34974122
-
Genetic and physiological determinants of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity.Mol Plant Pathol. 2009 Sep;10(5):579-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00561.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19694949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and identification of an endophytic bacteria Bacillus sp. K-9 exhibiting biocontrol activity against potato common scab.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jul 14;204(8):483. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02989-5. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35833995 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of the Bacillus SecYEG Pathway in Biosurfactant Production and Biofilm Formation.Int J Microbiol. 2024 May 2;2024:6627190. doi: 10.1155/2024/6627190. eCollection 2024. Int J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38725978 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogenesis and mechanical properties of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens biofilms: a comparative study of rough and smooth morphotypes.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025 May 10;8:100403. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2025.100403. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025. PMID: 40487030 Free PMC article.
-
Biological control of potato common scab and growth promotion of potato by Bacillus velezensis Y6.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 11;14:1295107. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1295107. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38149275 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus velezensis Y6, a Potential and Efficient Biocontrol Agent in Control of Rice Sheath Blight Caused by Rhizoctonia solani.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 16;12(8):1694. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081694. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203537 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol Effect of Bacillus velezensis D7-8 on Potato Common Scab and Its Complete Genome Sequence Analysis.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 28;13(4):770. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040770. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arseneault T., Goyer C., Filion M. (2016). Biocontrol of potato common scab is associated with high Pseudomonas fluorescens LBUM223 populations and phenazine-1-Carboxylic acid biosynthetic transcript accumulation in the potato geocaulosphere. Phytopathology 106 (9), 963–970. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-16-0019-R - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

