Role of Pharmacists in Antimicrobial Stewardship During COVID-19 Outbreak: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 36388623
- PMCID: PMC9656343
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S385170
Role of Pharmacists in Antimicrobial Stewardship During COVID-19 Outbreak: A Scoping Review
Abstract
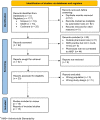
Since the beginning of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, pharmacists have been on the front lines of health care, offering vital services. Consequently, the need for pharmacists to support an effective antibiotic stewardship (AMS) program during the COVID-19 outbreak has become increasingly evident. This scoping review was performed to examine related articles in 2020-2022 published in the Scopus, SAGE, and Cochrane databases with the keywords "Pharmacist" and "Antibiotic Stewardship" and "COVID-19". The inclusion criteria were full-text articles written in English. A total of 15 articles were included in this review to describe the role of pharmacists in AMS during the COVID-19 outbreak. In general, pharmacists are responsible for identifying and treating patients during pandemics, ensuring the continued supply and accessibility of medications, promoting health policies, and monitoring antibiotic use for COVID-19 cases and co-infections. At the hospital, as the most significant element for pharmacists on the AMS team, the apparent change is demonstrated in educating patients on telehealth services, clarifying misconceptions about treatments and antibiotic consumption, as well as taking a leadership position to establish local guidelines for the COVID-19 treatment protocol. Pharmacists have an important role in the AMS program, and the COVID-19 pandemic was perceived as a highlight their importance. Therefore, their work with the AMS program needs to be improved as they learn to extend their role in telehealth services, educate and clarify the misconceptions about COVID-19 treatments and other antibiotic consumption in the community, inventory control the COVID-19 drug, antibiotics, and vaccine, as well as take the lead in establishing local guidelines on antibiotic consumption during the pandemic outbreak.
Keywords: COVID-19; antibiotic stewardship; pharmacists.
© 2022 Kusuma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacist-driven antimicrobial stewardship interventions in patients with COVID-19: a scoping review.Int J Clin Pharm. 2023 Jun;45(3):613-621. doi: 10.1007/s11096-023-01574-0. Epub 2023 May 10. Int J Clin Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37162655 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial stewardship implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the acute care settings: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2023 Feb 10;23(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15072-5. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36765323 Free PMC article.
-
Half of Prescribed Antibiotics Are Not Needed: A Pharmacist-Led Antimicrobial Stewardship Intervention and Clinical Outcomes in a Referral Hospital in Ethiopia.Front Public Health. 2020 Apr 9;8:109. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00109. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32328474 Free PMC article.
-
Expanded roles of community pharmacists in COVID-19: A scoping literature review.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2022 May-Jun;62(3):649-657. doi: 10.1016/j.japh.2021.12.013. Epub 2021 Dec 24. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2022. PMID: 35120863 Free PMC article.
-
Meeting the challenge for effective antimicrobial stewardship programs in regional, rural and remote hospitals - what can we learn from the published literature?Rural Remote Health. 2018 May;18(2):4442. doi: 10.22605/RRH4442. Epub 2018 May 24. Rural Remote Health. 2018. PMID: 29792036 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacist-driven antimicrobial stewardship interventions in patients with COVID-19: a scoping review.Int J Clin Pharm. 2023 Jun;45(3):613-621. doi: 10.1007/s11096-023-01574-0. Epub 2023 May 10. Int J Clin Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37162655 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the European Pharmacist in the Implementation of the Latest WHO Guidelines for Malaria.Pathogens. 2023 May 17;12(5):729. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050729. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37242399 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mothers in preventing tuberculosis in children: A scoping review.Narra J. 2024 Dec;4(3):e1062. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i3.1062. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39816113 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of the national antimicrobial stewardship competencies for UK undergraduate healthcare professional education within undergraduate pharmacy programmes: a survey of UK schools of pharmacy.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023 Aug 8;5(4):dlad095. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad095. eCollection 2023 Aug. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 37560542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collective remembering and future forecasting during the COVID-19 pandemic: how the impact of COVID-19 affected the themes and phenomenology of global and national memories across 15 countries - PubMed. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35817990/. Accessed November 3, 2022. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources