Effect of Pupil Size on Fixed-Luminance Flicker Full-Field Electroretinogram Magnitude
- PMID: 36389637
- PMCID: PMC9664919
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S382207
Effect of Pupil Size on Fixed-Luminance Flicker Full-Field Electroretinogram Magnitude
Abstract
Purpose: Diopsys® NOVA fixed-luminance flicker full-field electroretinogram (ffERG) device is a potential adjunct to conventional flicker ffERG testing for assessing cone cell function. Magnitude of measured electrical response is known to vary with pupil size in conventional ffERG testing. The index study characterizes the relationship between magnitude of measured electrical activity and pupil size, both pupil diameter and pupil area, for this device.
Methods: Seventeen patients (34 eyes) with no known ocular diseases were enrolled in the study. Electrophysiologic function of cone cells was evaluated using fixed-luminance flicker ffERG before and after dilation. Linear regression models, with inter-eye correlations controlled as fixed-effects, were used to characterize the effect of pupil dilation on the magnitude of the measured responses.
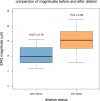
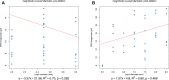
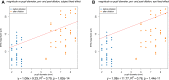
Results: Mean age of study patients was 33.5 (standard deviation 7.4 years), and 35.3% of the subjects were female. Mean value of electrical response magnitude was 10.07±2.79µV before dilation and 15.30±4.08µV after dilation. The correlations of ERG magnitude with pupil diameter and with pupil area were not significant for either dilated or undilated eyes considered separately but were highly significant (p<0.001) for dilated and undilated eyes considered in aggregate. ERG magnitude tended to increase by 1.08 µV for every 1 mm increase in pupillary diameter.
Conclusion: An increase in pupil size, both pupil diameter and pupil area, is significantly associated with an increase in flicker ffERG magnitude recorded by the Diopsys device, suggesting that pupil size should be measured and considered when making clinical judgments based on the flicker ffERGs recorded by the device, and that pupil size-specific reference ranges could improve the clinical utility of the device.
Keywords: Diopsys; ERG; electroretinogram; flicker ERG; magnitude; pupil.
© 2022 Mobasserian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

