Current landscape and future directions of bispecific antibodies in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 36389699
- PMCID: PMC9650279
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035276
Current landscape and future directions of bispecific antibodies in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
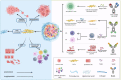
Recent advances in cancer immunotherapy using monoclonal antibodies have dramatically revolutionized the therapeutic strategy against advanced malignancies, inspiring the exploration of various types of therapeutic antibodies. Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are recombinant molecules containing two different antigens or epitopes identifying binding domains. Bispecific antibody-based tumor immunotherapy has gained broad potential in preclinical and clinical investigations in a variety of tumor types following regulatory approval of newly developed technologies involving bispecific and multispecific antibodies. Meanwhile, a series of challenges such as antibody immunogenicity, tumor heterogeneity, low response rate, treatment resistance, and systemic adverse effects hinder the application of BsAbs. In this review, we provide insights into the various architecture of BsAbs, focus on BsAbs' alternative different mechanisms of action and clinical progression, and discuss relevant approaches to overcome existing challenges in BsAbs clinical application.
Keywords: bispecific T cell engager; bispecific antibodies; cancer immunotherapy; clinical trials; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Copyright © 2022 Wei, Yang, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of insterest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

