New insights into iNKT cells and their roles in liver diseases
- PMID: 36389715
- PMCID: PMC9643775
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035950
New insights into iNKT cells and their roles in liver diseases
Abstract
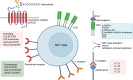
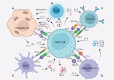
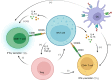
Natural killer T cells (NKTs) are an important part of the immune system. Since their discovery in the 1990s, researchers have gained deeper insights into the physiology and functions of these cells in many liver diseases. NKT cells are divided into two subsets, type I and type II. Type I NKT cells are also named iNKT cells as they express a semi-invariant T cell-receptor (TCR) α chain. As part of the innate immune system, hepatic iNKT cells interact with hepatocytes, macrophages (Kupffer cells), T cells, and dendritic cells through direct cell-to-cell contact and cytokine secretion, bridging the innate and adaptive immune systems. A better understanding of hepatic iNKT cells is necessary for finding new methods of treating liver disease including autoimmune liver diseases, alcoholic liver diseases (ALDs), non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLDs), and liver tumors. Here we summarize how iNKT cells are activated, how they interact with other cells, and how they function in the presence of liver disease.
Keywords: NKT cells; chemokine; cytokine; immune; liver diseases.
Copyright © 2022 Gu, Chu, Ma, Wang, Chen, Guan, Ren, Wu and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

