Dynamic and static biomechanical traits of cardiac fibrosis
- PMID: 36394025
- PMCID: PMC9659743
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1042030
Dynamic and static biomechanical traits of cardiac fibrosis
Abstract
Cardiac fibrosis is a common pathology in cardiovascular diseases which are reported as the leading cause of death globally. In recent decades, accumulating evidence has shown that the biomechanical traits of fibrosis play important roles in cardiac fibrosis initiation, progression and treatment. In this review, we summarize the four main distinct biomechanical traits (i.e., stretch, fluid shear stress, ECM microarchitecture, and ECM stiffness) and categorize them into two different types (i.e., static and dynamic), mainly consulting the unique characteristic of the heart. Moreover, we also provide a comprehensive overview of the effect of different biomechanical traits on cardiac fibrosis, their transduction mechanisms, and in-vitro engineered models targeting biomechanical traits that will aid the identification and prediction of mechano-based therapeutic targets to ameliorate cardiac fibrosis.
Keywords: biomechanical traits; cardiac fibrosis; mechanical model in vitro; mechanotransduction; myofibroblast.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Fan, Jin, Huang, Guo and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
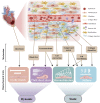


Similar articles
-
Mechanical communication in fibrosis progression.Trends Cell Biol. 2022 Jan;32(1):70-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34810063 Review.
-
The Soft- and Hard-Heartedness of Cardiac Fibroblasts: Mechanotransduction Signaling Pathways in Fibrosis of the Heart.J Clin Med. 2017 May 19;6(5):53. doi: 10.3390/jcm6050053. J Clin Med. 2017. PMID: 28534817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Featured Article: TGF-β1 dominates extracellular matrix rigidity for inducing differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Apr;243(7):601-612. doi: 10.1177/1535370218761628. Epub 2018 Mar 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29504479 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stress regulates the mechanotransduction and metabolism of cardiac fibroblasts in fibrotic cardiac diseases.Eur J Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;102(2):151288. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2023.151288. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Eur J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36696810 Review.
-
Exploring the cardiac ECM during fibrosis: A new era with next-gen proteomics.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 22;9:1030226. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1030226. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36483540 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts.Open Life Sci. 2025 Mar 11;20(1):20251063. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1063. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40092733 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of cardiac fibrosis for biomedical research.Smart Med. 2023 Aug 16;2(3):e20230020. doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20230020. eCollection 2023 Aug. Smart Med. 2023. PMID: 39188350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA CFRL aggravates cardiac fibrosis by modulating both miR-3113-5p/CTGF and miR-3473d/FN1 axis.iScience. 2023 Sep 25;26(10):108039. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108039. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37954142 Free PMC article.
-
Multiphysics simulations reveal haemodynamic impacts of patient-derived fibrosis-related changes in left atrial tissue mechanics.J Physiol. 2024 Dec;602(24):6789-6812. doi: 10.1113/JP287011. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39513553
-
Characterizing the Impact of Fabrication Methods on Mechanically Tunable Gelatin Hydrogels for Cardiac Fibrosis Studies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jul 13;12(7):759. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12070759. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andenæs K., Lunde I. G., Mohammadzadeh N., Dahl C. P., Aronsen J. M., Strand M. E., et al. (2018). The extracellular matrix proteoglycan fibromodulin is upregulated in clinical and experimental heart failure and affects cardiac remodeling. PLoS One 13 (7), e0201422. 10.1371/journal.pone.0201422 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashworth J. C., Thompson J. L., James J. R., Slater C. E., Pijuan-Galito S., Lis-Slimak K., et al. (2020). Peptide gels of fully-defined composition and mechanics for probing cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions in vitro . Matrix Biol. 85-86, 15–33. 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.06.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

